As if three cable faults within the Purple Sea weren’t sufficient of a headache, a sequence of West African cables have been broken on March 14.
The exact location and trigger of those faults aren’t identified right now, however let’s have a look at what we do know.
Which cables are broken?
Based mostly on experiences from a number of community operators within the area, the next cables are broken:
It isn’t clear right now if all 4 cables have been broken in the identical occasion or if some had pre-existing faults. These cables be part of the beforehand broken AAE-1, EIG, and SEACOM/TGN-Eurasia programs within the Purple Sea, which stay out of service.
Which international locations are most impacted?
Right now, there is not any official phrase on the fault places.
The Nigerian Communications Fee indicated the harm was someplace between Senegal and Côte d’Ivoire. Different experiences have recognized the situation as straight off Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire.
CloudFlare has noticed service disruptions for a number of international locations beginning south of Senegal, which can point out harm to a minimum of one cable someplace off the coast of Senegal and Gambia.
Assuming that’s the potential demarcation level for harm, right here’s an inventory of the coastal West African international locations south of this line, the variety of intercontinental cables linked to them, and their statuses:
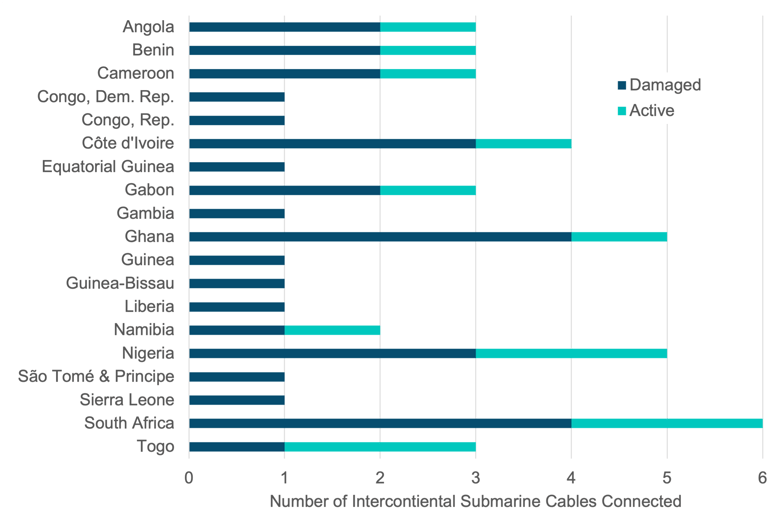
For West African international locations that rely solely on one of many broken cables, this doesn’t imply they’ve misplaced entry to intercontinental connectivity. They may ship visitors subsea or terrestrially to different international locations that retain intercontinental cable connectivity. Techniques nonetheless on-line embrace the brand new Equiano cable, in addition to EASSy, Glo-1, and Maroc Telecom West Africa.
Let’s additionally not neglect that landlocked African international locations like Botswana, Burkina Faso, Zambia, and Zimbabwe additionally depend on these cables for intercontinental connectivity and could also be impacted as nicely.
How lengthy will it take to repair these cables?
The time is takes to restore a cable depends upon on many components together with:
- Permits – upkeep vessels require permits from governments when repairs are required inside their waters.
- Loading – the restore vessel might want to go to a depot to load spare cable to accommodate the broken cable.
- Transit time – it takes time for a restore vessel to achieve the realm of suspected harm.
- Fault location – finding the broken portion of the cable just isn’t at all times straightforward as the situation of a cable might have shifted through the fault.
- Fault restore – the variety of fibers and kind of injury play a job in restore size.
- Climate window – earlier than a restore begins, upkeep firms should assess if the climate will stay appropriate for an extended sufficient interval to make the restore.
Repairs will virtually definitely be swifter for these West Africa cables in comparison with these within the Purple Sea, the place allowing challenges and ongoing Houthi assaults portend prolonged delays.
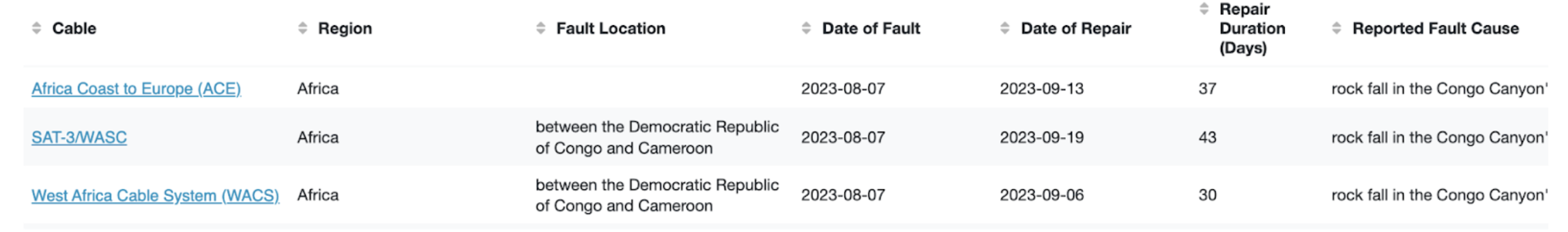
Whereas every restore scenario is exclusive, we will have a look at the August 2023 repairs off of the West African coast close to Angola and the Democratic Republic of Congo as a tough information. Based mostly on TeleGeography’s Submarine Cable Faults Database, the variety of days to restore these cables have been as follows:
- ACE – 37 days
- SAT-3/WASC – 43 days
- WACS – 30 days
TeleGeography’s Submarine Cable Faults Database
Be aware: The information proven is proscribed to what has been disclosed to the general public.
What’s the affect on customers and enterprises?
Community operators routinely carry their visitors throughout a number of cables in case of outages like this one. Numerous cable outages reduces the quantity of capability obtainable, which can degrade the standard of service. Nonetheless, it’s vital to have in mind which purposes and companies are used. In spite of everything, not all person exercise generates intercontinental visitors. Many companies will proceed to function usually.
On the time of writing, Amazon’s AWS cloud platform just isn’t reporting any points in South Africa, neither is Google Cloud. Microsoft has indicated some customers of their Azure cloud platform might expertise elevated latency and packet loss. The corporate acknowledged it’s including further capability and expects the issue to be resolved right now, March 15.
Can satellites clear up this drawback?
Probably not.
Submarine cables present way more bandwidth than satellites can. Satellites are definitely helpful in making certain important enterprise and governmental companies stay energetic if fiber connectivity is impaired or misplaced solely. Nonetheless, satellites are capacity-constrained.
Should you put collectively all of the capability from Starlink, Amazon Kuiper, and different new satellite tv for pc constellations, they might nonetheless account for lower than one-tenth the capability of a single, fashionable fiber-optic undersea cable.

