Replication is an important functionality in distributed programs to deal with challenges associated to fault tolerance, excessive availability, load balancing, scalability, information locality, community effectivity, and information sturdiness. It types a foundational factor for constructing strong and dependable distributed architectures. It is usually vital to have a number of choices (like regular and prefixless replication) to do the replication course of, since each resolution has its personal benefits.
Streams Replication Supervisor (SRM) is an enterprise-grade replication resolution that permits fault tolerant, scalable, and strong cross-cluster Kafka subject replication. SRM replicates information at excessive efficiency and retains subject properties in sync throughout clusters. Replication will be dynamically enabled for subjects and client teams. SRM additionally delivers customized extensions that facilitate set up, administration, and monitoring, making SRM a whole replication resolution that’s constructed for mission-critical workloads.
Introduction
Kafka as an occasion streaming element will be utilized to all kinds of use circumstances. SRM offers cross-cluster Kafka subject replication to make it extra fault tolerant and strong. SRM is predicated on the Mirror Maker 2 (MM2) element of Kafka, which is the improved model of Mirror Maker (MM1). MM1 has been used for years in large-scale manufacturing environments, however not with out a number of limitations—that’s the reason MM2 was launched.
These are a few of the MM1 limitations that MM2 addresses:
- Matters are created with default configuration, typically wanted to be repartitioned manually.
- ACL and configuration modifications aren’t synced throughout mirrored clusters. This makes it tough to handle a number of clusters.
- Data are repartitioned with DefaultPartitioner. Semantic partitioning could also be misplaced.
- Any configuration change means the cluster have to be bounced. This consists of including new subjects to the whitelist, which can be a frequent operation.
- No mechanism emigrate producers or customers between mirrored clusters.
- No assist for precisely as soon as supply. Data could also be duplicated throughout replication.
- Rebalancing causes latency spikes, which can set off additional rebalances.
When SRM replicates a subject, it renames the subject within the goal cluster by prefixing the identify of the subject with the alias (identify) of the supply cluster. This differs from the best way replication labored in MM1, the place the goal subjects had the identical identify because the supply (thus “prefixless”). The MM1 conduct is essential for some use-cases. For instance, cluster migration situations can’t be accurately carried out with the default replication conduct of SRM, the MM1 conduct is a should. Up till now, any such replication was not out there or absolutely supported. Furthermore, MM1 was deprecated in one of many newer releases of Kafka (Kafka 3.0.0) and its use is now not beneficial.
To handle this, Cloudera launched a brand new MM1-compatible mode in SRM. Beginning with Cloudera Information Platform (CDP) Non-public Cloud Base 7.1.9, prefixless replication is usually out there with replication monitoring assist in SRM. This makes it attainable emigrate cluster replication workloads from the deprecated MM1 to SRM with out change within the replicated subject names.
Replicated subject names
The naming of the replicated subjects is outlined by the replication coverage that SRM is configured to make use of. By default, SRM makes use of the DefaultReplicationPolicy, which provides the supply cluster alias as a prefix to the identify of replicated subjects. Prior to now, this was the one coverage out there natively in SRM and the design of the replication monitoring options within the service was primarily based on the belief that each replicated subject would at all times have a prefix. Due to this fact, SRM service position situations have been solely in a position to monitor replication flows that used a replication coverage that makes use of prefixes, such because the DefaultReplicationPolicy.
As soon as the IdentityReplicationPolicy was launched, customers have been in a position to replicate subjects with out having prefixes added to the replicated subject names. As a result of design of the SRM service although, these replications couldn’t be monitored till the discharge of CDP Non-public Cloud Base 7.1.9.
Be aware: SRM helps customized subject naming insurance policies by way of a plugin referred to as replication coverage. There are two totally different Replication coverage sorts shipped with SRM by default:
- DefaultReplicationPolicy – default coverage. Prefixes subject names with “<source_cluster>.”
- IdentityReplicationPolicy – coverage which doesn’t change subject names throughout replication. (with this coverage, replication monitoring doesn’t work till CDP 7.1.9 launch)
Distant subject discovery
SRM wants to have the ability to know which subjects are replicas and what are their respective supply subjects. It depends on the replication coverage and the subject naming conventions to find reproduction subjects by default. The method lists the entire subject names of a cluster, then detects the supply cluster identify. When utilizing the DefaultReplicationPolicy, SRM is aware of {that a} subject is a duplicate when it has a prefix that could be a legitimate cluster alias (<cluster_alias>.). The reproduction subject identify comprises the alias of the supply cluster and identify of the supply subject. For example, the subject identify will be source-cluster.topic-name. On this case source-cluster would be the alias of the supply cluster, whereas topic-name would be the identify of the subject within the supply cluster.
This discovery process has some limitations, because it depends on subject naming conventions to supply supply cluster data. When the IdentityReplicationPolicy is used, the supply cluster can’t be recognized by this methodology. Moreover, the present state of the replication (stopped, energetic, and many others.) has no reference to the reproduction subject detection—if a subject has been faraway from the SRM replication configuration, the logic will nonetheless detect the prefixed subject as a duplicate subject.
The above shortcomings have been addressed within the CDP Non-public Cloud Base 7.1.9. On this launch, SRM is shipped with a brand new property Use Inside Matter For Distant Matters Discovery, which is enabled for brand new installations. For upgraded clusters, this characteristic shall be disabled by default to make sure that present SRM deployments will proceed to work with out modifications in conduct.
When Use Inside Matter For Distant Matters Discovery is enabled, SRM drivers will write the listing of supply subject—goal subject pairs that should be replicated to an inside, compacted subject (srm-meta.inside), saved on the goal cluster. SRM drivers will periodically examine which subjects should be replicated and can write updates to the inner subject as wanted.
Shoppers attempting to find reproduction subjects are in a position to scan the “srm-meta.inside” subject, and eat the most recent message—which lists the presently replicated subjects. This information additionally comprises the source-target subject identify mappings. It makes the characteristic unbiased of the ReplicationPolicy that’s in use.
Prefixless replication
From CDP 7.1.9, SRM helps information replication, checkpointing, and monitoring with the IdentityReplicationPolicy. Identification replication, or prefixless replication, signifies that reproduction subjects’ names would be the identical as on the supply cluster (MM1-compatible mode, however with some great benefits of MM2). The IdentityReplicationPolicy will also be used for subject aggregation use circumstances, the place the identical subject on a number of clusters are replicated to the identical identically-named “aggregated subject” on a unique cluster. In fact, aggregation will be averted if DefaultReplicationPolicy is in use or if the separate supply clusters have totally different subject names.
To allow prefixless replication for SRM, you solely want to pick out the “Allow Prefixless Replication” property within the SRM service configuration.
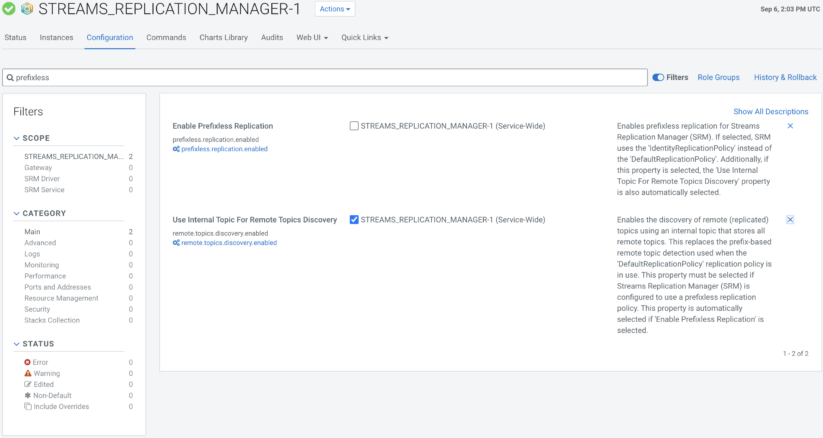
When “Allow Prefixless Replication” is chosen, SRM should additionally allow the “Use Inside Matter For Distant Matters Discovery” characteristic as a result of limitations of reproduction discovery talked about beforehand on this weblog. Thankfully, Cloudera Supervisor handles this robotically, so if a person allows the “Allow Prefixless Replication” choice, Cloudera Supervisor will override the configuration of “Use Inside Matter For Distant Matters Discovery” to allow it.
Prefixless replication will not be freed from limitations or caveats. Concentrate on the next:
- Replication loop detection will not be supported
Because of this, you have to make sure that subjects aren’t replicated in a loop between your supply and goal clusters. You’ll be able to guarantee this by organising your subject enable and deny lists (also called subject filters) in a means that’s applicable on your use case.
For instance, assume you could have two replications that replicate subjects between two clusters, however in numerous instructions. If each replications embody topic_1, they need to by no means be enabled on the identical time.
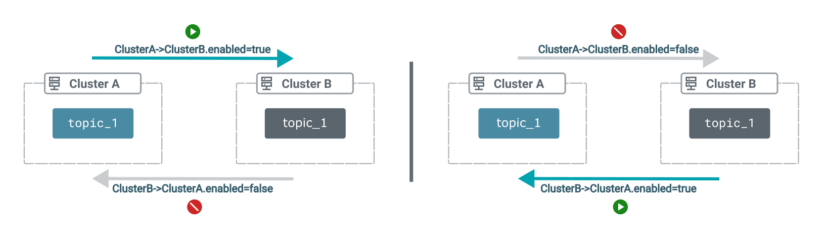
- All SRM providers should use the identical replication coverage
For instance, if you wish to use prefixless replication then the entire SRM providers ought to use IdentityReplicationPolicy. In case of prefixed replication DefaultReplicationPolicy needs to be used in all places. Clusters related by replication flows, whatever the variety of SRM providers, ought to solely use one ReplicationPolicy. In any other case, replications shall be combined up and undesirable unintended effects can occur.
- Group offset sync needs to be disabled
SRM makes a mapping about Kafka message offsets of the supply and goal clusters. Offset checkpoints are saved within the supply clusters and they are going to be interpreted provided that the message is coming from the present supply cluster. If extra supply clusters have the identical group offsets, then they’ll intrude with one another, so group offset sync needs to be disabled.
- Not all REST API endpoints and SMM UI options are supported
- The /v2/topic-metrics/{goal}/{downstreamTopic}/{metric} endpoint of the SRM Service v2 API doesn’t work correctly with prefixless replication. Use the /v2/topic-metrics/{supply}/{goal}/{upstreamTopic}/{metric} endpoint as an alternative.
- The replication metric graphs proven on the Matter Particulars web page of the SMM UI don’t work with prefixless replication. The graph will not be displayed.
Abstract
Prefixless replication lets you use MM1-like replication conduct in CDP whereas getting access to the numerous enterprise prepared options that SRM offers. Whereas aggregation is the primary use case for prefixless replication, it will also be used to construct conventional replication pipelines that present a security web on your Kafka information if issues go amiss. Higher but, prefixless replication can be an ideal device emigrate that previous Kafka deployment working on CDH, HDP, or HDF to CDP.
As well as, the modifications and enhancements to distant subject discovery that have been launched alongside prefixless replication make SRM extra strong than ever as some core options inside SRM, like replication monitoring, now not must depend on subject prefixes to operate.
If you wish to study extra about SRM and Kafka in CDP Non-public Cloud Base, jump over to Cloudera’s doc portal and see Streams Messaging Ideas, Streams Messaging How Tos, and/or the Streams Messaging Migration Information. That is the primary of a two-blog sequence, to proceed your journey on Streams Replication, click on right here.
To get fingers on with SRM, obtain Cloudera Stream Processing Group version right here.
Thinking about becoming a member of Cloudera?
At Cloudera, we’re engaged on fine-tuning huge information associated software program bundles (primarily based on Apache open-source initiatives) to supply our clients a seamless expertise whereas they’re working their analytics or machine studying initiatives on petabyte-scale datasets. Verify our web site for a take a look at drive!
If you’re taken with huge information, wish to know extra about Cloudera, or are simply open to a dialogue with techies, go to our fancy Budapest workplace at our upcoming meetups. Or, simply go to our careers web page, and turn out to be a Clouderan!

