
Current variations of the Raspberry Robin malware are stealthier and implement one-day exploits which might be deployed solely on methods which might be vulnerable to them.
One-day exploits discuss with code that leverages a vulnerability that the developer of the impacted software program patched not too long ago however the repair has both not been deployed to all shoppers or it has not been utilized on all susceptible methods.
From the second the seller discloses the vulnerability, which normally comes with publishing a patch, risk actors rush to create an exploit and use it earlier than the repair propagates to a lot of methods.
In line with a report from Verify Level, Raspberry Robin has not too long ago used not less than two exploits for 1-day flaws, which signifies that the malware operator both has the potential to develop the code or has sources that present it.
Raspberry Robin background
Raspberry Robin is a worm that Pink Canary, a managed detection and response firm, first recognized in 2021. It spreads primarily via detachable storage units akin to USB drives to determine a foothold on contaminated methods and facilitate the deployment of extra payloads.
It has been related to risk actors like EvilCorp, FIN11, TA505, the Clop ransomware gang, and different malware operations, however its creators and maintainers are unknown.
Since its discovery, Raspberry Robin has repeatedly advanced, including new options, evasion strategies, and adopting a number of distribution strategies. One instance of evasion trick it applied was to drop faux payloads to mislead researchers.
Verify Level stories that it has noticed an uptick in Raspberry Robin’s operations beginning October 2023, with giant assault waves focusing on methods worldwide.
A notable swap in current campaigns is the usage of the Discord platform to drop malicious archive information onto the goal, possible after emailing the hyperlinks to the goal.
The archives comprise a digitally signed executable (OleView.exe) and a malicious DLL file (aclui.dll) that’s side-loaded when the sufferer runs the executable, thus activating Raspberry Robin within the system.
Focusing on n-day flaws
When Raspberry Robin is first run on a pc, it should mechanically try to elevate privileges on the gadget utilizing quite a lot of 1-day exploits.
Verify Level highlights that the brand new Raspberry Robin marketing campaign leverages exploits for CVE-2023-36802, and CVE-2023-29360, two native privilege escalation vulnerabilities in Microsoft Streaming Service Proxy and the Home windows TPM Machine Driver.
In each circumstances, the researchers say, Raspberry Robin began exploiting the issues utilizing a then-unknown exploit lower than a month after the safety points had been disclosed publicly, on June 13 and September 12, 2023.
As illustrated within the timeline diagram under, Raspberry Robin exploited the 2 flaws earlier than safety researchers first printed proof of idea exploit code for the 2 flaws.

Particularly, relating to CVE-2023-36802, which allows attackers to escalate their privileges to the SYSTEM degree, Cyfirma reported that an exploit had been obtainable for buy on the Darkish Net since February 2023, a full seven months earlier than Microsoft acknowledged and addressed the difficulty.
This timeline means that Raspberry Robin acquires 1-day exploits from exterior sources virtually instantly after their disclosure, as their price as zero days is probably going an excessive amount of even for bigger cybercrime operations.
Verify Level discovered proof that factors to this principle as effectively, for the reason that exploits utilized by Raspberry Robin weren’t embedded into the principle 32-bit part, however deployed as exterior 64-bit executables, and likewise lack the heavy obfuscation sometimes seen with this malware.
New evasion mechanisms
Verify Level’s report additionally highlights a number of developments within the newest Raspberry Robin variants, which embrace new anti-analysis, evasion, and lateral motion mechanisms.
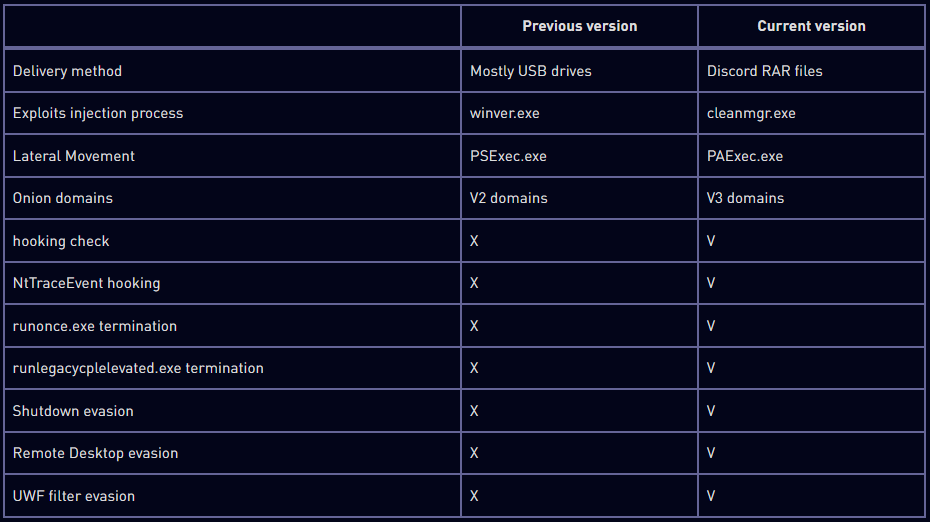
To evade safety instruments and OS defenses, the malware now makes an attempt to terminate particular processes like ‘runlegacycplelevated.exe,’ associated to Use Account Management (UAC), and patches the NtTraceEvent API to evade detection by Occasion Tracing for Home windows (ETW).
Furthermore, Raspberry Robin now checks if sure APIs, like ‘GetUserDefaultLangID’ and ‘GetModuleHandleW’, are hooked by evaluating the primary byte of the API perform to detect any monitoring processes by safety merchandise.
One other fascinating new tactic is the implementation of routines that use APIs like ‘AbortSystemShutdownW’ and ‘ShutdownBlockReasonCreate’ to stop system shutdowns that would interrupt the malware’s exercise.
To hide the command and management (C2) addresses, the malware first randomly engages with one of many 60 hard-coded Tor domains pointing to well-known websites to make preliminary communications seem benign.
Lastly, Raspberry Robin now makes use of PAExec.exe as an alternative of PsExec.exe to obtain the payload immediately from the internet hosting location. This choice was possible made to extend its stealth, as PsExec.exe is thought to be misused by hackers.
The researchers imagine that Raspberry Robin will maintain evolving and add new exploits to its arsenal, in search of code that has not been launched publicly. Primarily based on observations through the malware evaluation, it’s possible that the operators of the malware doesn’t create is linked to a developer that gives the exploit code.
Verify Level’s report supplies an inventory of indicators of compromise for Raspberry Robin, which consists in hashes for the malware, a number of domains in the Tor community, and Discord URLs for downloading the malicious archive.
