
Practically 52,000 internet-exposed Tinyproxy cases are susceptible to CVE-2023-49606, a just lately disclosed vital distant code execution (RCE) flaw.
Tinyproxy is an open-source HTTP and HTTPS proxy server designed to be quick, small, and light-weight. It’s particularly tailor-made for UNIX-like working methods and is often used by small companies, public WiFi suppliers, and residential customers.
Firstly of the month, Cisco Talos disclosed CVE-2023-49606, a vital (CVSS v3: 9.8) use-after-free flaw the researchers found in December 2023, impacting variations 1.11.1 (newest) and 1.10.0, after claiming to not receiving a response from the builders.
Cisco’s report shared detailed details about the vulnerability, together with proof-of-concept exploits that crashed the server and will doubtlessly result in distant code execution.
Talos researchers defined within the report that the flaw happens within the ‘remove_connection_headers()’ operate, the place particular HTTP headers (Connection and Proxy-Connection) will not be appropriately managed, resulting in reminiscence being freed after which incorrectly accessed once more.
This might be simply exploited with a easy malformed HTTP request (e.g., Connection: Connection) with out requiring authentication.
Cisco warned on the time that regardless of its efforts to alert Tinyproxy’s builders of the vital flaw, it acquired no response, and no patch was out there for customers to obtain.
On Saturday, Censys reported seeing 90,000 internet-exposed Tinyproxy providers on-line, of which about 57% have been susceptible to CVE-2023-49606.
Particularly, Censys discovered 18,372 cases working the susceptible model 1.11.1 and one other 1,390 working on 1.10.0.
Most of those cases are positioned in america (11,946), adopted by South Korea (3,732), China (675), France (300), and Germany (150).
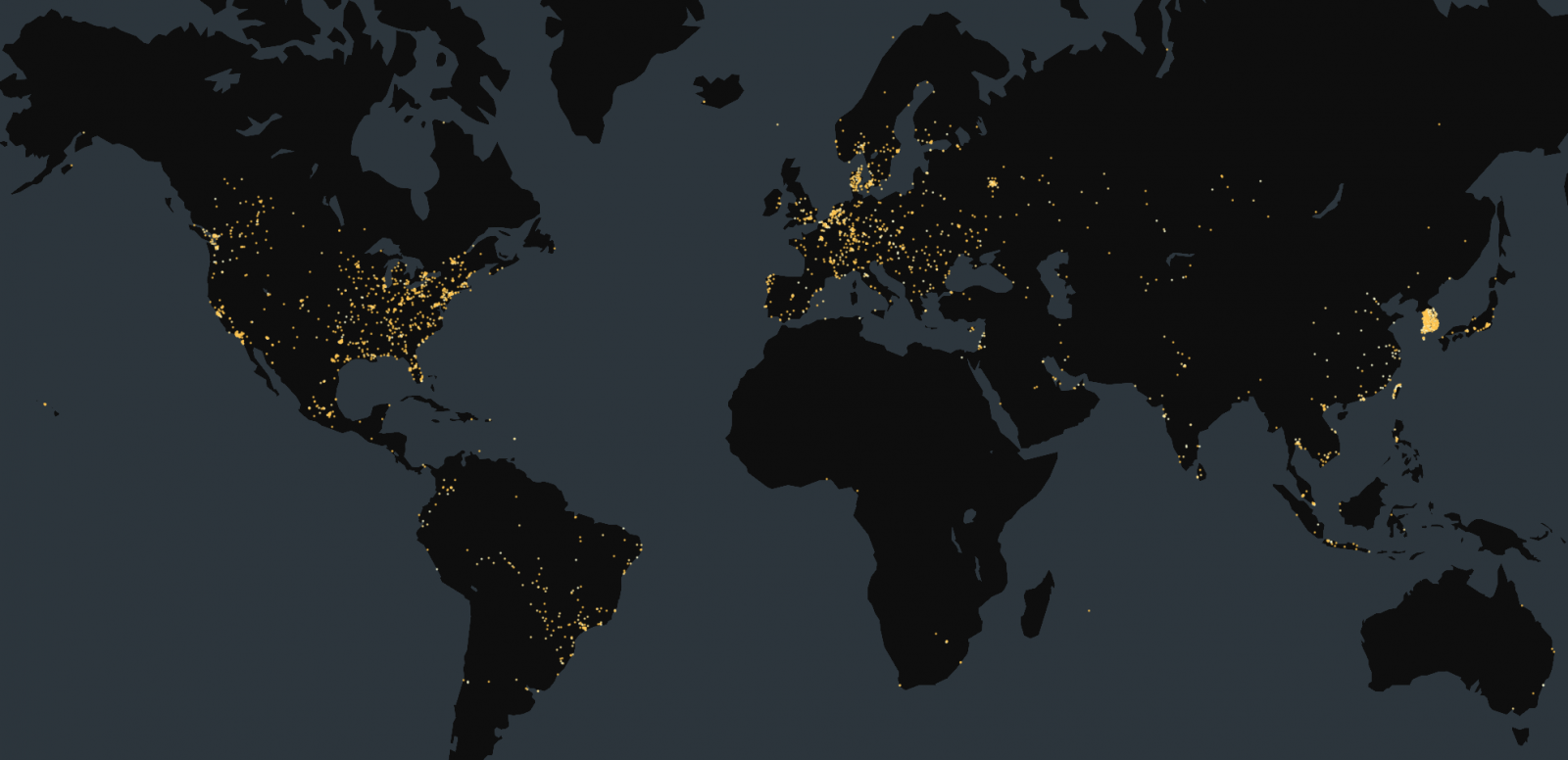
Supply: Censys
Flaw fastened
On Sunday, 5 days after Cisco disclosed the bug, the maintainers of Tinyproxy launched a repair for CVE-2023-49606, which adjusts reminiscence administration as wanted to forestall exploitation.
Nevertheless, the Tinyproxy maintainer disputed that Cisco correctly disclosed the bug, stating they by no means acquired the report through the undertaking’s requested disclosure channels.
“A safety researcher from TALOS intelligence discovered a use-after-free vulnerability in tinyproxy in december 2023, claiming to have contacted upstream and waited 6 months for publication,” famous the builders on GitHub
“No matter he did to contact upstream, it wasn’t efficient and never what was described on both the tinyproxy homepage nor in README.md.”
“He definitely did not strive laborious to discover a responsive contact, and doubtless pulled a random e mail deal with out of git log and despatched a mail there. The vulnerability was made public on might 01 2024, and it took a full 5 days till i used to be notified on IRC by a distro bundle maintainer.”
The commit (12a8484) containing the safety repair is within the upcoming model 1.11.2, however folks in pressing want can pull the change from the grasp department or manually apply the highlighted repair.
“This can be a fairly nasty bug, and will doubtlessly result in RCE – although i have not seen a working exploit but,” continued the Tinyproxy maintainers.
“What it definitely permits is a DOS assault on the server if tinyproxy is both utilizing musl libc 1.2+ – whose hardened reminiscence allocator routinely detects UAF, or constructed with an deal with sanitizer.”
The builders additionally famous that the up to date code solely triggers after passing authentication and entry listing checks, that means the vulnerability may not have an effect on all setups, particularly these inside managed environments like company networks or these utilizing fundamental authentication with safe passwords.
