
Two zero-day vulnerabilities affecting Ivanti’s Join Safe VPN and Coverage Safe community entry management (NAC) home equipment at the moment are below mass exploitation.
As found by menace intelligence firm Volexity, which additionally first noticed the zero-days being utilized in assaults since December, a number of menace teams chain the CVE-2023-46805 authentication bypass and the CVE-2024-21887 command injection vulnerabilities in widespread assaults beginning January 11.
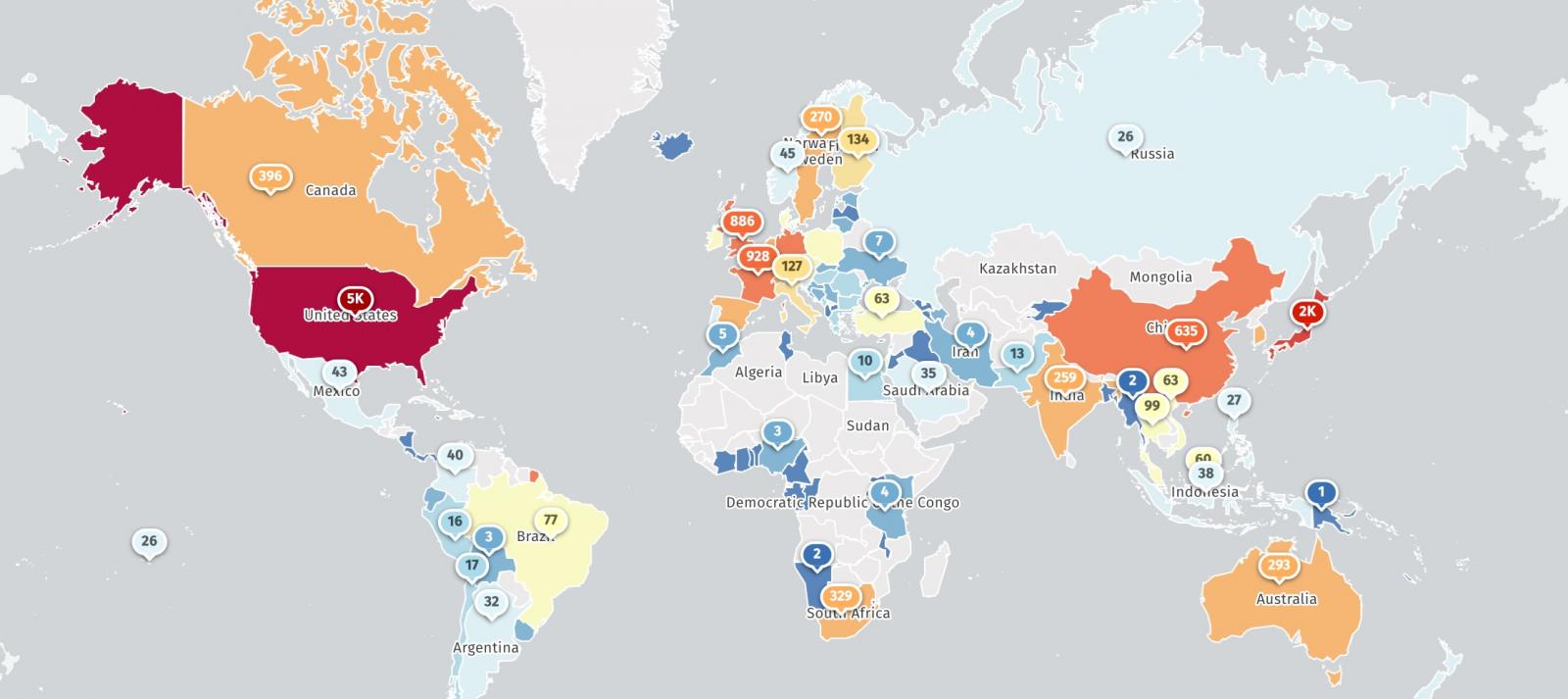
“Victims are globally distributed and differ vastly in measurement, from small companies to a number of the largest organizations on the earth, together with a number of Fortune 500 corporations throughout a number of trade verticals,” Volexity warned in the present day.
The attackers backdoored their targets’ techniques utilizing a GIFTEDVISITOR webshell variant which was discovered on a whole bunch of home equipment.
“On Sunday, January 14, 2024, Volexity had recognized over 1,700 ICS VPN home equipment that have been compromised with the GIFFEDVISITOR webshell. These home equipment seem to have been indiscriminately focused, with victims everywhere in the world,” Volexity mentioned.
The checklist of victims found by Volexity up to now consists of authorities and navy departments worldwide, nationwide telecommunications corporations, protection contractors, expertise corporations, banking, finance, and accounting organizations, worldwide consulting outfits, and aerospace, aviation, and engineering corporations.
Whereas Ivanti is but to launch patches for these two actively exploited zero-days, admins are suggested to use mitigation measures supplied by the seller on all ICS VPNs on their community.
They need to additionally run Ivanti’s Integrity Checker Instrument and contemplate all knowledge on the ICS VPN equipment (together with passwords and any secrets and techniques) as compromised if indicators of a breach are discovered, as detailed within the ‘Responding to Compromise’ part of Volexity’s earlier weblog publish.
Risk monitoring service Shadowserver presently tracks greater than 16,800 ICS VPN home equipment uncovered on-line, virtually 5,000 in the US (Shodan additionally sees over 15,000 Web-exposed Ivanti ICS VPNs).
As Ivanti disclosed final week, attackers can run arbitrary instructions on all supported variations of ICS VPN and IPS home equipment when efficiently chaining the 2 zero days.
Assaults have now escalated from a restricted variety of clients impacted by assaults exploiting these vulnerabilities, with the suspected Chinese language state-backed menace actor (tracked as UTA0178 or UNC5221) now being joined by a number of others.
As Mandiant additionally revealed on Friday, its safety consultants discovered 5 customized malware strains deployed on breached clients’ techniques with the top aim of dropping webshells, extra malicious payloads, and stealing credentials.
The checklist of instruments used within the assaults consists of:
- Zipline Passive Backdoor: customized malware that may intercept community site visitors, helps add/obtain operations, creates reverse shells, proxy servers, server tunneling
- Thinspool Dropper: customized shell script dropper that writes the Lightwire net shell onto Ivanti CS, securing persistence
- Wirefire net shell: customized Python-based net shell supporting unauthenticated arbitrary command execution and payload dropping
- Lightwire net shell: customized Perl net shell embedded in a authentic file, enabling arbitrary command execution
- Warpwire harvester: customized JavaScript-based instrument for harvesting credentials at login, sending them to a command and management (C2) server
- PySoxy tunneler: facilitates community site visitors tunneling for stealthiness
- BusyBox: multi-call binary combining many Unix utilities utilized in varied system duties
- Thinspool utility (sessionserver.pl): used to remount the filesystem as ‘learn/write’ to allow malware deployment
Essentially the most notable is ZIPLINE, a passive backdoor that intercepts incoming community site visitors and offers file switch, reverse shell, tunneling, and proxying capabilities.
Suspected Chinese language hacking teams used one other ICS zero-day tracked as CVE-2021-22893 two years in the past to breach dozens of U.S. and European authorities, protection, and monetary organizations.
Final yr, beginning in April, two different zero-days (CVE-2023-35078 and CVE-2023-35081) in Ivanti’s Endpoint Supervisor Cellular (EPMM) have been tagged as actively exploited and later reported as being used to breach a number of Norwegian authorities organizations.
One month later, hackers began utilizing a 3rd zero-day flaw (CVE-2023-38035) in Ivanti’s Sentry software program to bypass API authentication on susceptible gadgets in restricted and focused assaults.
