Methane emissions are liable for almost a 3rd of the overall warming the planet has skilled to date. Whereas there are pure sources of the greenhouse gasoline, together with wetlands, human actions like agriculture and fossil-fuel manufacturing have dumped thousands and thousands of metric tons of extra methane into the ambiance. The focus of methane has greater than doubled over the previous 200 years. However there are nonetheless giant uncertainties about the place, precisely, emissions are coming from.
Answering these questions is a difficult however essential first step to chopping emissions and addressing local weather change. To take action, researchers are utilizing instruments starting from satellites just like the not too long ago launched MethaneSAT to floor and aerial surveys.
The US Environmental Safety Company estimates that roughly 1% of oil and gasoline produced winds up leaking into the ambiance as methane air pollution. However survey after survey has steered that the official numbers underestimate the true extent of the methane drawback.
For the websites examined within the new examine, “methane emissions look like increased than authorities estimates, on common,” says Evan Sherwin, a analysis scientist at Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory, who carried out the evaluation as a postdoctoral fellow at Stanford College.
The info Sherwin used comes from one of many largest surveys of US fossil-fuel manufacturing websites thus far. Beginning in 2018, Kairos Aerospace and the Carbon Mapper Mission mapped six main oil- and gas-producing areas, which collectively account for about 50% of onshore oil manufacturing and about 30% of gasoline manufacturing. Planes flying overhead gathered almost 1 million measurements of effectively websites utilizing spectrometers, which might detect methane utilizing particular wavelengths of sunshine.
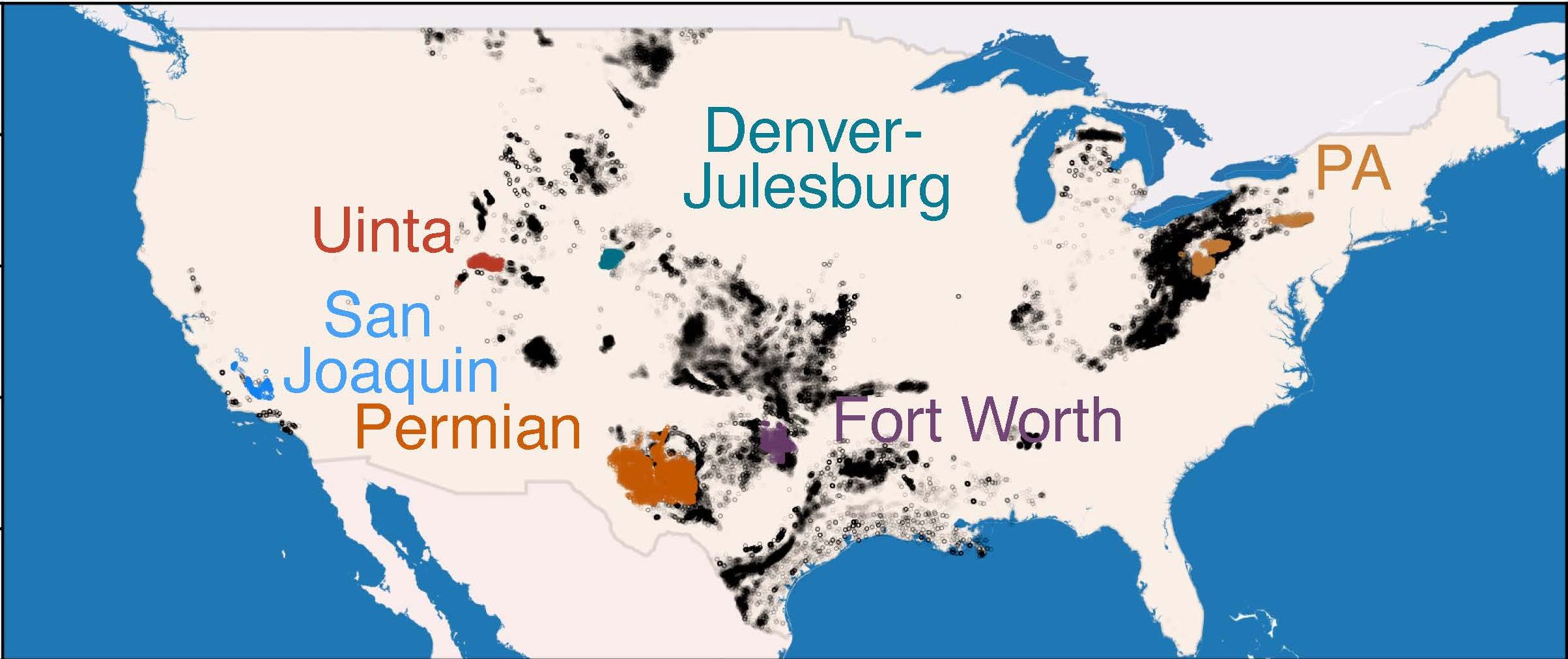
Right here’s the place issues get difficult. Methane sources in oil and gasoline manufacturing are available all styles and sizes. Some small wells slowly leak the gasoline at a charge of roughly one kilogram of methane an hour. Different sources are considerably greater, emitting tons of and even hundreds of kilograms per hour, however these leaks could final for under a brief interval.
The planes utilized in these surveys detect largely the biggest leaks, above roughly 100 kilograms per hour (although they catch smaller ones typically, right down to round one-tenth that measurement, Sherwin says). Combining measurements of those giant leak websites with modeling to estimate smaller sources, researchers estimated that the bigger leaks account for an outsize proportion of emissions. In lots of circumstances, round 1% of effectively websites could make up over half the overall methane emissions, Sherwin says.
However some scientists say that this and different research are nonetheless restricted by the measurement instruments accessible. “This is a sign of the present know-how limits,” says Ritesh Gautam, a lead senior scientist on the Environmental Protection Fund.
