
The mini mild follower robotic proposed right here works in ambient mild. It employs sensors to detect variations in mild depth, which permits it to navigate and carry out duties in various environments.
This mini-robot exploration combines robotics and light-sensing expertise, showcasing the potential for autonomous methods to adapt to altering mild circumstances. The block diagram of the light-follower robotic is proven in Fig. 1.
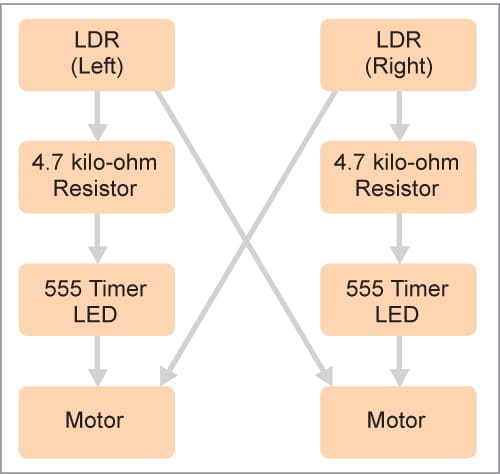
This mini-robot introduces a fascinating exploration into the realm of robotics by combining the light-dependent resistor (LDR) and the 555 timer IC. The core idea entails making a light-activated robotic, the place the LDR capabilities because the sensory ‘eyes,’ and the 555 timer serves because the controlling ‘mind.’
As mild depth adjustments, the resistance values of the LDR detect these variations, prompting the 555 timers to orchestrate the robotic’s actions. The result’s a robotic that dynamically responds to its surroundings, shifting in coordination with the presence or absence of sunshine.
This hands-on endeavor offers a foundational understanding of sensors, timers, and motor management, bridging the hole between idea and sensible software.
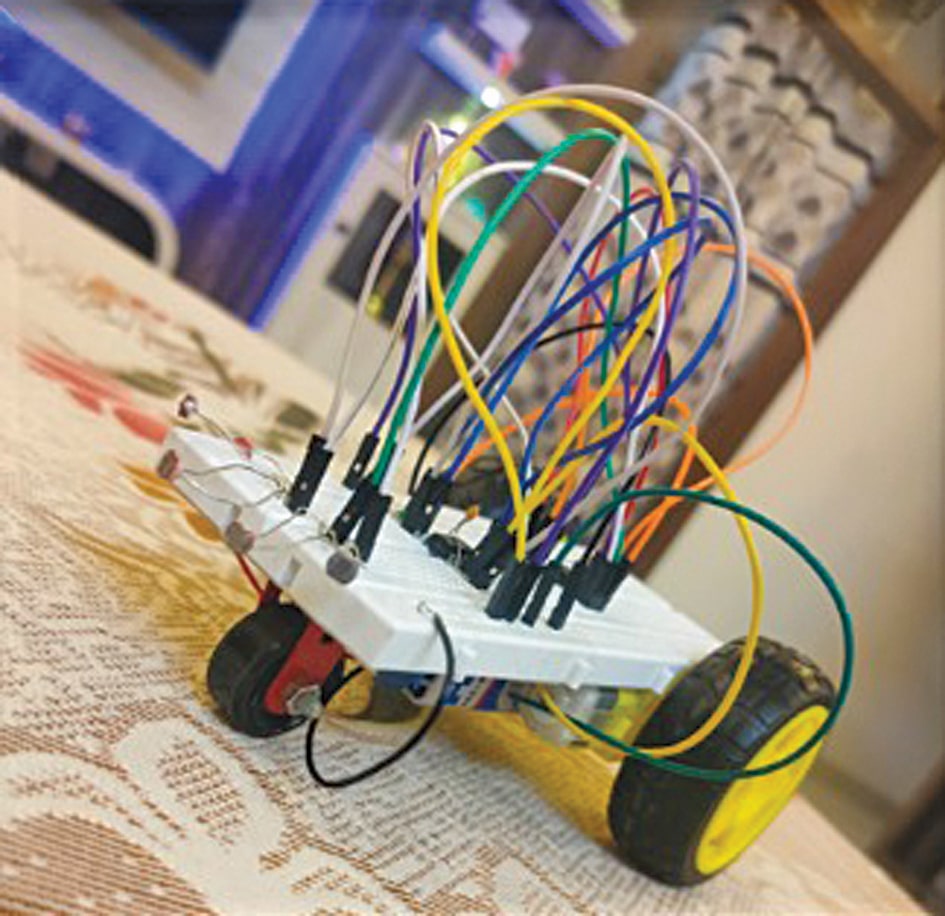
The sunshine follower robotic’s prototype on a breadboard is proven in Fig. 2.
Gentle Follower Robotic Circuit and Working
Fig. 2 exhibits the circuit diagram of the light-following robotic. It’s constructed round two 555 timers (IC1, IC2), two DC motors (M1, M2), two light-dependent resistors (LDR1, LDR2), and some different parts. For the ability provide, a 9V energy adaptor or a 9V battery could also be used.
| Components Record | |
| Semiconductors: | |
| IC1, IC2 | -555 timer |
| Resistors (all 1/4-watt, ±5% carbon): | |
| R1-R4 | -4.7-kilo-ohm |
| Capacitors: | |
| C1, C2 | -0.01µF polyester |
| Miscellaneous: | |
| LDR1, LDR2 | -Gentle-dependent resistor |
| M1, M2 | -12V DC motor |
| -Robotic meeting | |
| -Two wheels | |
| -One small shifting wheel | |
| -Jumper wires, male-to-male | |
| -Breadboard | |
| -9V DC battery/adaptor | |
The concept behind the light-activated robotic is to create a flexible and adaptive robotic system that may reply to adjustments in lighting circumstances. Gentle sensors allow the robotic to understand its environment and make selections accordingly.
The circuit includes two divisions: one is LDR, the light-sensing factor, and the opposite is the 555 activator. The LDR1 is paired with resistor R1 to type a possible divider to feed the set off voltage to the IC 555 (IC1). It provides most voltage when no mild is incident on it and minimal voltage when mild falls on the LDR.

The resistance of the LDR is inversely proportional to the depth of sunshine falling on it. It implies that if the depth of incident mild is excessive, the resistance of the LDR might be much less, and vice versa.
The activator is constructed round a 555 IC, which is wired as an astable multivibrator. This precept is used right here to make the 555 act as a change when mild is incident on the LDR.
The working of this robotic is straightforward. Timer IC 555 will get activated when its discharge pin 7 receives a voltage larger than 0.8V. As soon as the IC is activated, the voltage at pins 2 and 6 must be between 1/third and a couple of/third of the availability voltage for the output to be excessive.
For instance, if the voltage at discharge pin 7 is above 0.8V, and the voltage at pins 2 and 6 is half the availability voltage, the output goes excessive to show the motor.
Within the circuit, a voltage divider is created utilizing the LDR and a resistor. It’s then related to the 555 timer IC. When it’s darkish, the LDR’s resistance will increase, and the voltage on the voltage divider drops beneath 0.8V, inflicting the 555 timer IC output to go low to show off the motor.
When there may be sufficient mild, the voltage on the discharge pin 7 goes above 0.8V, and the 555 IC output goes excessive to activate the motor.
Development and Testing
Earlier than assembling the circuit based mostly on the circuit diagram proven in Fig. 3, additionally confer with Fig. 2. This can give an actual thought concerning the building of the robotic. Assemble the circuit immediately on the breadboard and use a cupboard and wheels in such a approach that the robotic can easily transfer when mild falls on the LDRs. LDRs are mounted on the highest of the breadboard in such a approach that mild ought to fall on them for the right motion of the robotic.
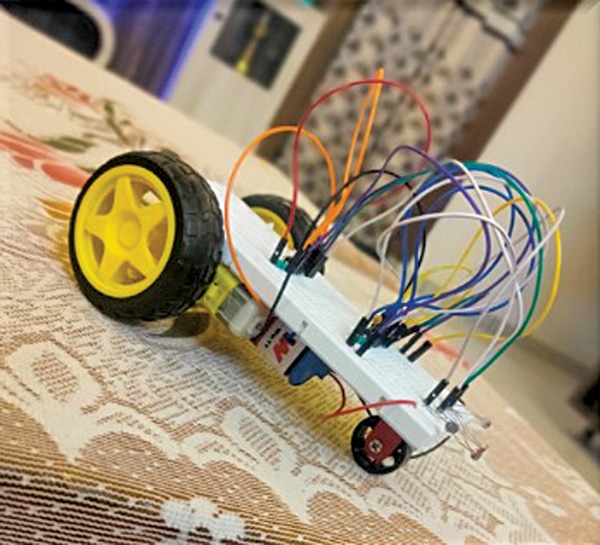

After correct meeting, your light-activated robotic is able to use. When mild falls on LDR1 or LDR2, respective motors rotate accordingly, ensuing within the robotic’s motion. A picture of a ready-to-use robotic on a breadboard is proven in Fig. 4.
Authors: Manmohan Singh, Vivek Gowda, Ramiksha Shetty, and Sahana P from the Electronics and Communication Division, Sapthagiri School of Engineering, Bengaluru
