Customers are more and more recognizing that knowledge decay and temporal depreciation are main dangers for companies, consequently constructing options with low knowledge latency, schemaless ingestion and quick question efficiency utilizing SQL, corresponding to supplied by Rockset, turns into extra important.
Rockset gives the power to JOIN knowledge throughout a number of collections utilizing acquainted SQL be part of varieties, corresponding to INNER, OUTER, LEFT and RIGHT be part of. Rockset additionally helps a number of JOIN methods to fulfill the JOIN kind, corresponding to LOOKUP, BROADCAST, and NESTED LOOPS. Utilizing the proper kind of JOIN with the proper JOIN technique can yield SQL queries that full in a short time. In some circumstances, the sources required to run a question exceeds the quantity of obtainable sources on a given Digital Occasion. In that case you possibly can both improve the CPU and RAM sources you utilize to course of the question (in Rockset, meaning a bigger Digital Occasion) or you possibly can implement the JOIN performance at knowledge ingestion time. A lot of these JOINs can help you commerce the compute used within the question to compute used throughout ingestion. This can assist with question efficiency when question volumes are greater or question complexity is excessive.
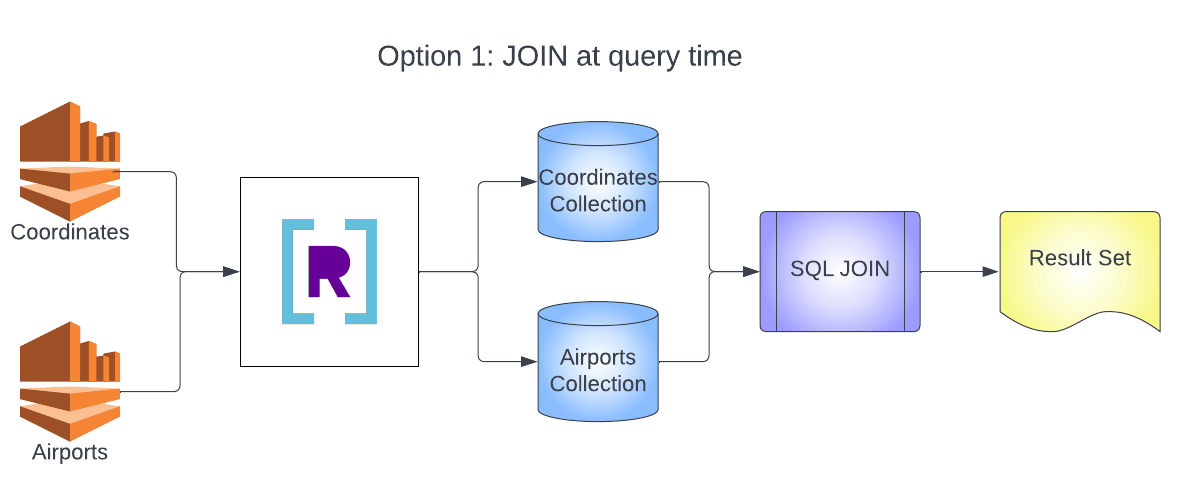
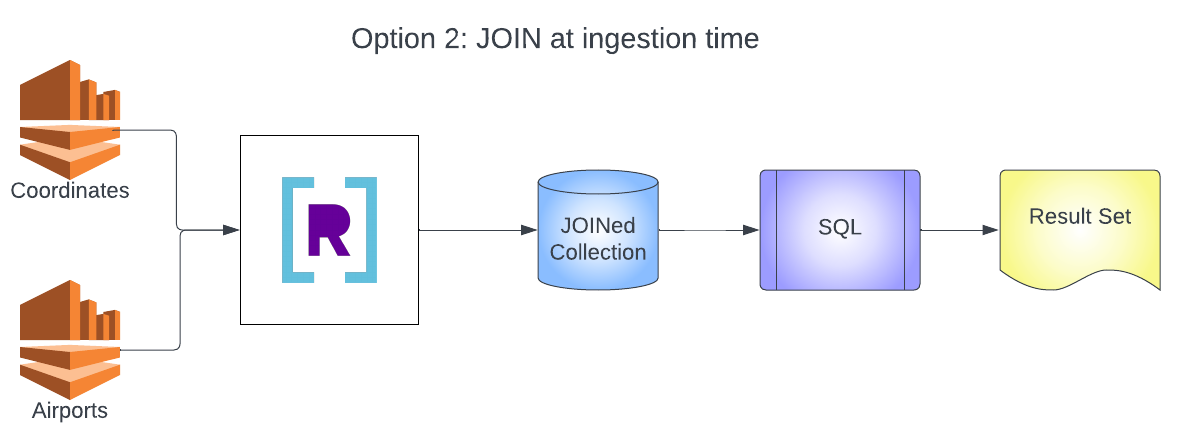
This doc will cowl constructing collections in Rockset that make the most of JOINs at question time and JOINs at ingestion time. It’ll examine and distinction the 2 methods and checklist among the tradeoffs of every strategy. After studying this doc it’s best to be capable of construct collections in Rockset and question them with a JOIN, and construct collections in Rockset that JOIN at ingestion time and challenge queries in opposition to the pre-joined assortment.
Answer Overview
You’ll construct two architectures on this instance. The primary is the everyday design of a number of knowledge sources going into a number of collections after which JOINing at question time. The second is the streaming JOIN structure that may mix a number of knowledge sources right into a single assortment and mix information utilizing a SQL transformation and rollup.
Dataset Used
We’re going to use the dataset for airways accessible at: 2019-airline-delays-and-cancellations.
Stipulations
- Kinesis Knowledge Streams configured with knowledge loaded
- Rockset group created
- Permission to create IAM insurance policies and roles in AWS
- Permissions to create integrations and collections in Rockset
Should you need assistance loading knowledge into Amazon Kinesis you need to use the next repository. Utilizing this repository is out of scope of this text and is just supplied for instance.
Walkthrough
Create Integration
To start this primary you have to arrange your integration in Rockset to permit Rockset to connect with your Kinesis Knowledge Streams.
- Click on on the integrations tab.

- Choose Add Integration.
- Choose Amazon Kinesis from the checklist of Icons.

- Click on Begin.
-
Comply with the on display screen directions for creating your IAM Coverage and Cross Account function.
a.Your coverage will appear to be the next:{ "Model": "2012-10-17", "Assertion": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "kinesis:ListShards", "kinesis:DescribeStream", "kinesis:GetRecords", "kinesis:GetShardIterator" ], "Useful resource": [ "arn:aws:kinesis:*:*:stream/blog_*" ] } ] } - Enter your Function ARN from the cross account function and press Save Integration.
Create Particular person Collections
Create Coordinates Assortment
Now that the combination is configured for Kinesis, you possibly can create collections for the 2 knowledge streams.
- Choose the Collections tab.

- Click on Create Assortment.

- Choose Kinesis.

- Choose the combination you created within the earlier part
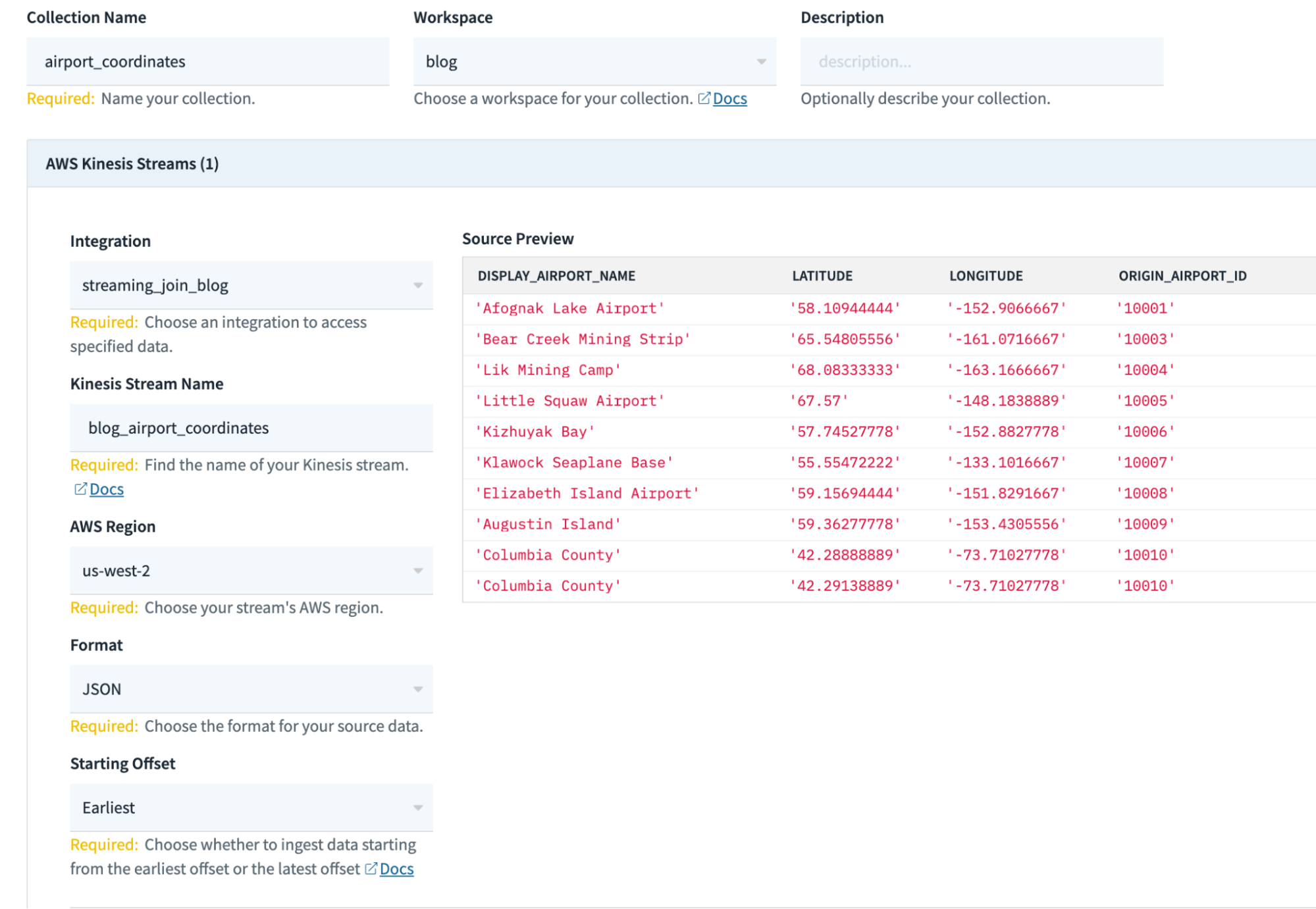
- On this display screen, fill within the related details about your assortment (some configurations could also be completely different for you):
Assortment Identify: airport_coordinates
Workspace: commons
Kinesis Stream Identify: blog_airport_coordinates
AWS area: us-west-2
Format: JSON
Beginning Offset: Earliest
- Scroll right down to the Configure ingest part and choose Assemble SQL rollup and/or transformation.

-
Paste the next SQL Transformation within the SQL Editor and press Apply.
a. The next SQL Transformation will solid the
LATITUDEandLONGITUDEvalues as floats as an alternative of strings as they arrive into the gathering and can create a brand new geopoint that can be utilized to question in opposition to utilizing spatial knowledge queries. The geo-index will give sooner question outcomes when utilizing capabilities likeST_DISTANCE()than constructing a bounding field on latitude and longitude.
SELECT
i.*,
try_cast(i.LATITUDE as float) LATITUDE,
TRY_CAST(i.LONGITUDE as float) LONGITUDE,
ST_GEOGPOINT(
TRY_CAST(i.LONGITUDE as float),
TRY_CAST(i.LATITUDE as float)
) as coordinate
FROM
_input i
- Choose the Create button to create the gathering and begin ingesting from Kinesis.
Create Airports Assortment
Now that the combination is configured for Kinesis you possibly can create collections for the 2 knowledge streams.
- Choose the Collections tab.

- Click on Create Assortment.

- Choose Kinesis.

- Choose the combination you created within the earlier part.

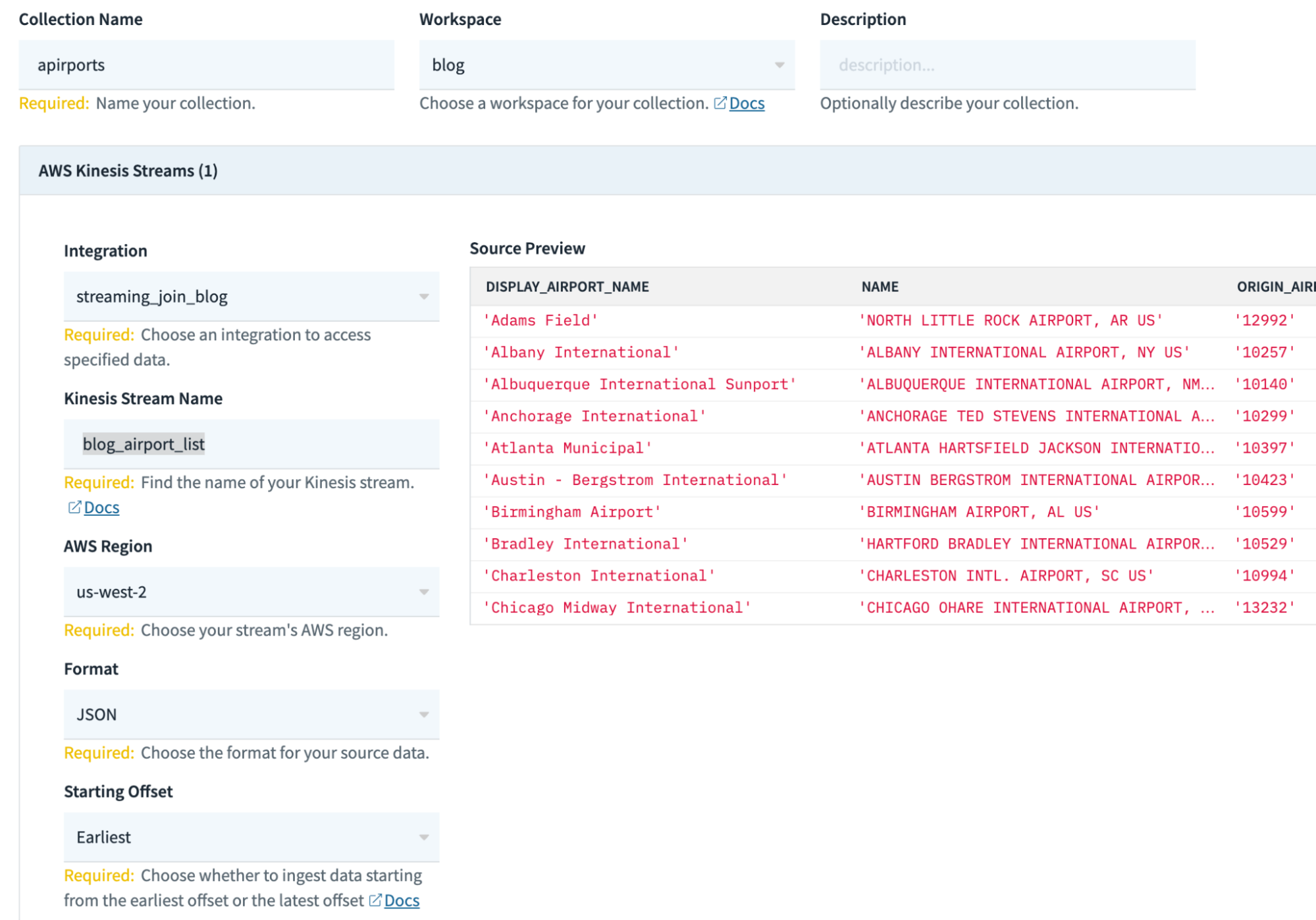
- On this display screen, fill within the related details about your assortment (some configurations could also be completely different for you):
Assortment Identify: airports
Workspace: commons
Kinesis Stream Identify: blog_airport_list
AWS area: us-west-2
Format: JSON
Beginning Offset: Earliest
- This assortment doesn’t want a SQL Transformation.
- Choose the Create button to create the gathering and begin ingesting from Kinesis.
Question Particular person Collections
Now you’ll want to question your collections with a JOIN.
- Choose the Question Editor

- Paste the next question:
SELECT
ARBITRARY(a.coordinate) coordinate,
ARBITRARY(a.LATITUDE) LATITUDE,
ARBITRARY(a.LONGITUDE) LONGITUDE,
i.ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID,
ARBITRARY(i.DISPLAY_AIRPORT_NAME) DISPLAY_AIRPORT_NAME,
ARBITRARY(i.NAME) NAME,
ARBITRARY(i.ORIGIN_CITY_NAME) ORIGIN_CITY_NAME
FROM
commons.airports i
left outer be part of commons.airport_coordinates a
on i.ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID = a.ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID
GROUP BY
i.ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID
ORDER BY i.ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID
- This question will be part of collectively the airports assortment and the airport_coordinates assortment and return the results of all of the airports with their coordinates.
If you’re questioning about the usage of ARBITRARY on this question, it’s used on this case as a result of we all know that there can be just one LONGITUDE (for instance) for every ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID. As a result of we’re utilizing GROUP BY, every attribute within the projection clause must both be the results of an aggregation operate, or that attribute must be listed within the GROUP BY clause. ARBITRARY is only a helpful aggregation operate that returns the worth that we count on each row to have. It is considerably a private alternative as to which model is much less complicated — utilizing ARBITRARY or itemizing every row within the GROUP BY clause. The outcomes would be the similar on this case (keep in mind, just one LONGITUDE per ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID).
Create JOINed Assortment
Now that you simply see how you can create collections and JOIN them at question time, you’ll want to JOIN your collections at ingestion time. This may can help you mix your two collections right into a single assortment and enrich the airports assortment knowledge with coordinate data.
- Click on Create Assortment.

- Choose Kinesis.

- Choose the combination you created within the earlier part.
- On this display screen fill within the related details about your assortment (some configurations could also be completely different for you):
Assortment Identify: joined_airport
Workspace: commons
Kinesis Stream Identify: blog_airport_coordinates
AWS area: us-west-2
Format: JSON
Beginning Offset: Earliest
- Choose the + Add Further Supply button.

- On this display screen, fill within the related details about your assortment (some configurations could also be completely different for you):
Kinesis Stream Identify: blog_airport_list
AWS area: us-west-2
Format: JSON
Beginning Offset: Earliest
- You now have two knowledge sources able to stream into this assortment.
- Now create the SQL Transformation with a rollup to
JOINthe 2 knowledge sources and press Apply.
SELECT
ARBITRARY(TRY_CAST(i.LONGITUDE as float)) LATITUDE,
ARBITRARY(TRY_CAST(i.LATITUDE as float)) LONGITUDE,
ARBITRARY(
ST_GEOGPOINT(
TRY_CAST(i.LONGITUDE as float),
TRY_CAST(i.LATITUDE as float)
)
) as coordinate,
COALESCE(i.ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID, i.OTHER_FIELD) as ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID,
ARBITRARY(i.DISPLAY_AIRPORT_NAME) DISPLAY_AIRPORT_NAME,
ARBITRARY(i.NAME) NAME,
ARBITRARY(i.ORIGIN_CITY_NAME) ORIGIN_CITY_NAME
FROM
_input i
group by
ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID
- Discover the important thing that you’d usually
JOINon is used because theGROUP BYdiscipline within the rollup. A rollup creates and maintains solely a single row for each distinctive mixture of the values of the attributes within theGROUP BYclause. On this case, since we’re grouping on just one discipline, the rollup may have just one row perORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID. Every incoming knowledge will get aggregated into the row for its correspondingORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID. Though the information in every stream is completely different, they each have values forORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID, so this successfully combines the 2 knowledge sources and creates distinct information primarily based on everyORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID. - Additionally discover the projection:
COALESCE(i.ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID,i.OTHER_FIELD) asORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID,
a. That is used for instance within the occasion that yourJOINkeys will not be named the identical factor in every assortment.i.OTHER_FIELDdoesn’t exist, howeverCOALESCEwith discover the primary non-NULL worth and use that because the attribute toGROUPon orJOINon. - Discover the aggregation operate
ARBITRARYis doing one thing greater than standard on this case.ARBITRARYprefers a worth over null. If, after we run this method, the primary row of knowledge that is available in for a givenORIGIN_AIRPORT_IDis from the Airports knowledge set, it is not going to have an attribute forLONGITUDE. If we question that row earlier than the Coordinates document is available in, we count on to get a null forLONGITUDE. As soon as a Coordinates document is processed for thatORIGIN_AIRPORT_IDwe wish theLONGITUDEto at all times have that worth. SinceARBITRARYprefers a worth over a null, as soon as now we have a worth forLONGITUDEit is going to at all times be returned for that row.
This sample assumes that we cannot ever get a number of LONGITUDE values for a similar ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID. If we did, we would not ensure of which one could be returned from ARBITRARY. If a number of values are potential, there are different aggregation capabilities that may probably meet our wants, like, MIN() or MAX() if we wish the biggest or smallest worth now we have seen, or MIN_BY() or MAX_BY() if we needed the earliest or newest values (primarily based on some timestamp within the knowledge). If we wish to gather the a number of values that we’d see of an attribute, we will use ARRAY_AGG(), MAP_AGG() and/or HMAP_AGG().
- Click on Create Assortment to create the gathering and begin ingesting from the 2 Kinesis knowledge streams.
Question JOINed Assortment
Now that you’ve created the JOINed assortment, you can begin to question it. You need to discover that within the earlier question you have been solely capable of finding information that have been outlined within the airports assortment and joined to the coordinates assortment. Now now we have a set for all airports outlined in both assortment and the information that’s accessible is saved within the paperwork. You’ll be able to challenge a question now in opposition to that assortment to generate the identical outcomes because the earlier question.
- Choose the Question Editor.

- Paste the next question:
SELECT
i.coordinate,
i.LATITUDE,
i.LONGITUDE,
i.ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID,
i.DISPLAY_AIRPORT_NAME,
i.NAME,
i.ORIGIN_CITY_NAME
FROM
commons.joined_airport i
the place
NAME is just not null
and coordinate is just not null
ORDER BY i.ORIGIN_AIRPORT_ID
- Now you might be returning the identical end result set that you simply have been earlier than with out having to challenge a
JOIN. You might be additionally retrieving fewer knowledge rows from storage, making the question probably a lot sooner.The velocity distinction might not be noticeable on a small pattern knowledge set like this, however for enterprise purposes, this method may be the distinction between a question that takes seconds to 1 that takes a number of milliseconds to finish.
Cleanup
Now that you’ve created your three collections and queried them you possibly can clear up your deployment by deleting your Kinesis shards, Rockset collections, integrations and AWS IAM function and coverage.
Evaluate and Distinction
Utilizing streaming joins is a good way to enhance question efficiency by transferring question time compute to ingestion time. This may scale back the frequency compute must be consumed from each time the question is run to a single time throughout ingestion, ensuing within the general discount of the compute crucial to attain the identical question latency and queries per second (QPS). However, streaming joins is not going to work in each state of affairs.
When utilizing streaming joins, customers are fixing the information mannequin to a single JOIN and denormalization technique. This implies to make the most of streaming joins successfully, customers must know quite a bit about their knowledge, knowledge mannequin and entry patterns earlier than ingesting their knowledge. There are methods to deal with this limitation, corresponding to implementing a number of collections: one assortment with streaming joins and different collections with uncooked knowledge with out the JOINs. This enables advert hoc queries to go in opposition to the uncooked collections and identified queries to go in opposition to the JOINed assortment.
One other limitation is that the GROUP BY works to simulate an INNER JOIN. If you’re doing a LEFT or RIGHT JOIN you won’t be able to do a streaming be part of and should do your JOIN at question time.
With all rollups and aggregations, it’s potential you possibly can lose granularity of your knowledge. Streaming joins are a particular form of aggregation that won’t have an effect on knowledge decision. However, if there’s an impression to decision then the aggregated assortment is not going to have the granularity that the uncooked collections would have. This may make queries sooner, however much less particular about particular person knowledge factors. Understanding these tradeoffs will assist customers resolve when to implement streaming joins and when to stay with question time JOINs.
Wrap-up
You have got created collections and queried these collections. You have got practiced writing queries that use JOINs and created collections that carry out a JOIN at ingestion time. Now you can construct out new collections to fulfill use circumstances with extraordinarily small question latency necessities that you’re not in a position to obtain utilizing question time JOINs. This information can be utilized to resolve real-time analytics use circumstances. This technique doesn’t apply solely to Kinesis, however may be utilized to any knowledge sources that assist rollups in Rockset. We invite you to seek out different use circumstances the place this ingestion becoming a member of technique can be utilized.
For additional data or assist, please contact Rockset Help, or go to our Rockset Group and our weblog.
Rockset is the main real-time analytics platform constructed for the cloud, delivering quick analytics on real-time knowledge with stunning effectivity. Study extra at rockset.com.
