A sufficiently highly effective quantum pc holds the potential to interrupt as we speak’s encryption, making all digital communication across the globe weak to cyberattacks. Despite the fact that the transition from present noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) computer systems—susceptible to errors and measurement constraints—to these able to threatening present cryptographic requirements is predicted to take years and even many years, a current surge in analysis, experimentation, and funding in quantum tech suggests the chance will not be as far-off because it as soon as appeared.
Quantum computing has the potential to form not solely cryptography and cybersecurity, however main fields akin to software program optimization, chip design, and sophisticated system modeling, amongst many others.
Although engineers as we speak have entry to quantum circuit libraries, quantum simulators, and even actual quantum computer systems (by way of the cloud), the leap to quantum computing represents a definite shift from conventional computing paradigms. On this article, Toptal quantum engineers goal to demystify the present state of quantum computing: why it issues, the way it diverges from conventional computing, and the probabilities it unlocks. Moreover, they focus on sensible sources akin to Cirq and TensorFlow Quantum that allow hands-on expertise with quantum computing.
The Energy of Quantum Computing: Why Quantum Issues
Think about an enormous library crammed with hundreds of books. You already know that the library accommodates the answer you might want to a selected drawback, however you don’t know wherein e-book or in what mixture of books you’ll find it. Every e-book represents a potential resolution.
To search out the answer, you might have a single scholar undergo the books one after the other, sentence by sentence, till they come across it. However this course of, except they’re extraordinarily lucky, will likely be impractically time-consuming. The bigger the library, the extra complicated the search will likely be.
Now think about a scholar with the magical skill to test all of the books concurrently. They don’t should undergo the method sequentially, seeing as a substitute a transparent image of the whole library and its contents without delay. Naturally, they are going to attain the answer a lot sooner than the nonmagical scholar.
Conventional computing operates like the primary scholar. It excels at duties that may be carried out in a simple, sequential method, however struggles as the issues develop into extra complicated and require the exploration of many potentialities concurrently.
Quantum computing, however, gives a number of algorithms that enable for a sooner processing of information in comparison with classical computer systems. Within the context of our analogy, an instance is Grover’s search algorithm, able to finding a desired merchandise inside a big database considerably sooner than classical computing can. It does so by utilizing quantum properties akin to superposition and interference, which we take a better take a look at later on this article.
This permits a quadratic speedup over classical search algorithms for unstructured knowledge, which is actually as quick as quantum algorithms can theoretically get for this type of drawback. For structured search, wherein extra details about the dataset is on the market, different quantum algorithms can outperform Grover’s. An instance is Shor’s algorithm, which might issue massive integers and clear up discrete logarithm issues exponentially sooner than classical algorithms.
Quantum Options for Quantum Issues
Quantum computing is effectively on its strategy to remodeling various fields, and cryptography and cybersecurity are amongst these almost certainly to be disrupted by this know-how. Algorithms like RSA encryption, the underpinning of a lot of as we speak’s digital safety, depend on the truth that factoring a sufficiently massive quantity to interrupt one in every of its cases utilizing classical computer systems can take centuries. This sort of job, nonetheless, is a specialty of Shor’s algorithm; working on a sufficiently steady quantum pc, this algorithm has the theoretical skill to interrupt these encryption schemes in mere hours or days.
The potential is so actual that the Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Know-how (NIST) has been growing algorithms resistant to those assaults for years, integrating them right into a post-quantum cryptographic customary to maintain data property safe even after large-scale quantum computer systems have been constructed. The World Financial Discussion board estimates that greater than 20 billion digital units will should be changed or up to date within the subsequent 10 to twenty years to permit for brand new types of quantum-resistant encrypted communication.
New communication strategies and protocols are additionally being developed in an effort to safe programs additional. Quantum key distribution (QKD), for instance, depends on the foundations of quantum mechanics to permit two events to create a shared secret key, enabling them to speak securely, whereas ongoing analysis into quantum safe direct communication protocols goals to facilitate the direct and safe transmission of knowledge.
Cybersecurity will not be the one discipline that’s certain to reap the advantages of quantum-first approaches. Quantum computing additionally holds nice potential in healthcare. Joao Diogo de Oliveira explains that its skill to simulate molecular interactions in unprecedented element can speed up drug discovery. “By leveraging quantum algorithms, we are able to discover huge chemical areas extra effectively and predict molecular behaviors with larger accuracy. Quantum computer systems can carry out complicated simulations that allow extra exact identification of potential drug candidates. This reduces the time and value of early drug growth phases. Moreover, quantum-enhanced ML fashions can analyze massive datasets to establish patterns that classical strategies miss, bettering drug efficacy and security predictions. This integration has the potential to convey revolutionary therapies to market sooner than ever,” he says.
Quantum algorithms like Grover’s and quantum annealing are additionally more likely to have a significant influence on optimization issues, thus serving to to seek out extra environment friendly options for large-scale, complicated logistics, finance, and scheduling challenges. However the influence of quantum computing will not be restricted to sensible purposes; it additionally extends to total industries and scientific disciplines. Fields akin to supplies science, renewable vitality analysis, local weather modeling, and particle physics might all profit from advances in quantum computing energy.
Quantum Computing: Historical past and Present State
The idea of quantum computing, as soon as unique to the realm of theoretical physics, started to take tangible form within the early Nineteen Eighties, because of pioneers like Nobel Prize laureate Richard Feynman and Paul Dirac Prize winner David Deutsch who envisioned machines that may make use of quantum mechanics to achieve beforehand unattainable processing energy. By 1996, a staff led by IBM physics researcher Isaac Chuang had developed the world’s first quantum pc, able to dealing with simply two quantum bits, or “qubits”—subatomic particles which might be the quantum equal of the standard bit, and the fundamental unit of quantum computing.
Chuang’s system manipulated particular person atoms of hydrogen and chlorine inside chloroform, making them operate as a pc. Though the system remained steady for just a few nanoseconds and was restricted to fixing easy issues, this achievement confirmed that quantum know-how was not simply theoretical.
By the late 2010s, there have been quantum processors that would function on 50 to 72 qubits, and in 2023 IBM introduced IBM Quantum Condor, a quantum processor of 1,000+ qubits, together with a smaller processor, the IBM Quantum Heron. Each can run or simulate parallel processes, with the smaller Heron being a lot much less susceptible to errors and sooner general than Condor, bringing the sensible purposes of quantum computing a lot nearer to actuality.
These are fairly important developments within the discipline. Nonetheless, it ought to be famous that the quantum computer systems we’ve as we speak are nonetheless not highly effective or steady sufficient to actually compete in opposition to classical computer systems to unravel complicated issues and course of the numerous quantities of information that may distinguish them from conventional machines. Right now’s quantum computer systems are principally used for analysis functions. The quantum pc revolution continues to be some time away, however quantum operations could be simulated on classical computer systems, and builders can attempt their hand at quantum computing because of various instruments out there available on the market.
The Fundamentals of Quantum Mechanics: Superposition, Entanglement, and Interference
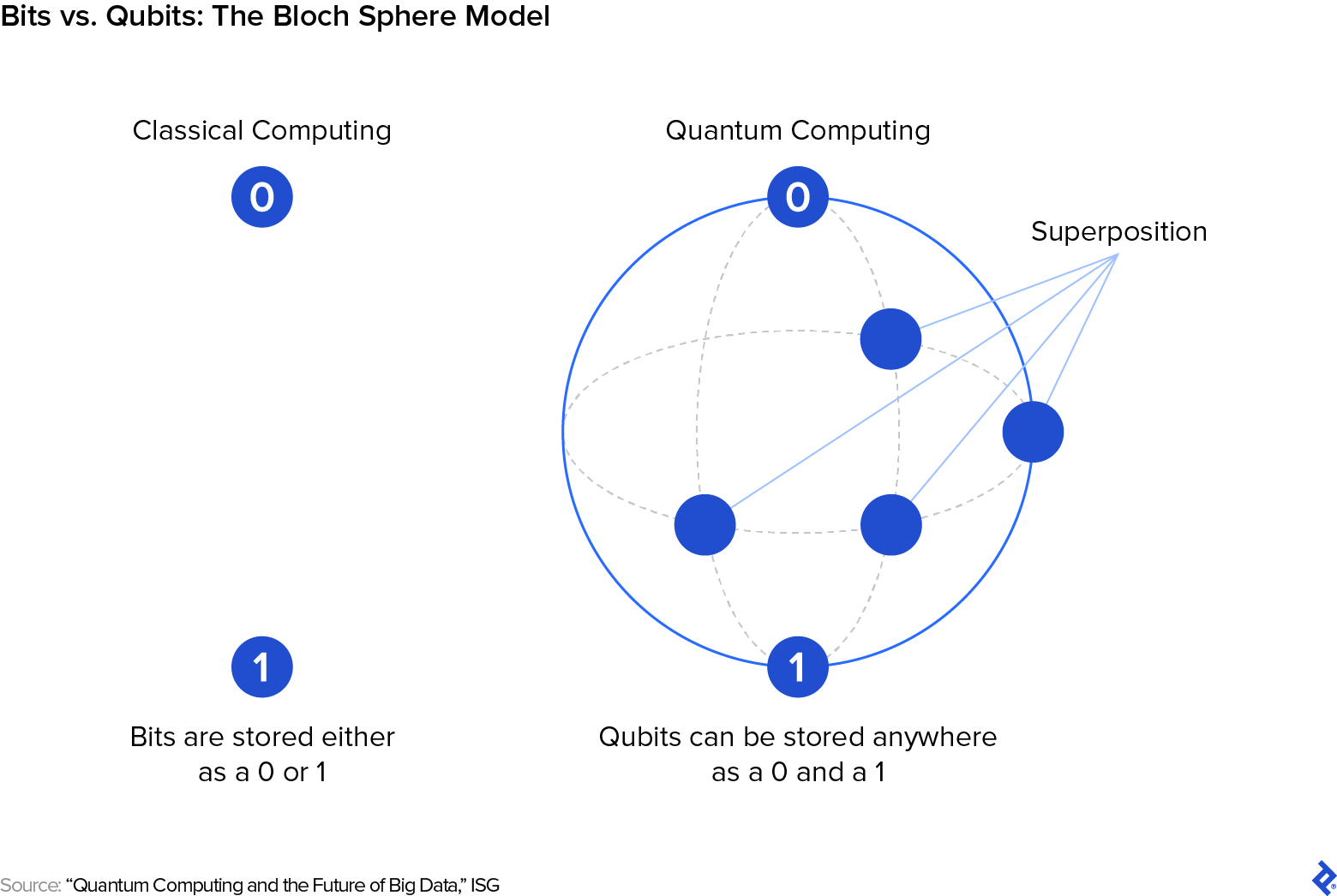
Quantum computing is odd. The science powering its capabilities is counterintuitive as a result of it differs considerably from the legal guidelines that govern our day-to-day interactions with the world. Classical data processing operates on bits which might be both off or on, representing two potential values, 0 or 1. All classical computations could be damaged down into operations with these binary values.
However a quantum processor makes use of qubits. These elementary items can exist in a state of quantum superposition, wherein they aren’t both 0 or 1 however maintain each potentialities on the similar time. This isn’t only a third state however a continuum of possible states wherein a qubit can embody each potential mixture of 0 and 1 to various levels.
Nephtali Garrido-Gonzalez explains that the variety of potential states a quantum pc can characterize grows exponentially with every added qubit. “For instance, two qubits can characterize 4 states concurrently, three can characterize eight states, and so forth, rising as 2^n, the place n is the variety of qubits. That’s the reason, for some particular calculations, quantum computing is so compelling.”
|
Variety of Qubits |
Potential Unbiased States |
|
1 |
[0], [1] |
|
2 |
[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1] |
|
3 |
[0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 1] [1, 0, 0], [1, 1, 0], [1, 0, 1], [1, 1, 1] |
A standard strategy to characterize qubits is the Bloch sphere. Image the poles of this sphere as our classical 0 and 1. A classical bit should be on the north pole (0) or the south pole (1), however qubits in superposition can exist anyplace on the sphere’s floor, opening up an array of logical states way more quite a few than the binarism utilized by classical computer systems.
Different tips up the qubit’s sleeve push computational effectivity even additional: The property of entanglement allows a qubit to immediately affect the state of one other, irrespective of the gap between them. Entangled particles could be put at reverse extremes of the universe, and they might nonetheless act in unison.
4 states could be created from the maximal entanglement of two qubits. These states are often called Bell states, and they’re the only instance of quantum entanglement. Every state is linked to the opposite and utterly correlated no matter distance, making all states “maximally entangled.”
The 4 states could be mathematically represented as:
|
|Φ⁺⟩ = (|00⟩ + |11⟩) / √2 |
|
|Φ⁻⟩ = (|00⟩ – |11⟩) / √2 |
|
|Ψ⁺⟩ = (|01⟩ + |10⟩) / √2 |
|
|Ψ⁻⟩ = (|01⟩ – |10⟩) / √2 |
Right here, |0⟩ and |1⟩ are the fundamental states of a qubit, and the symbols + and – point out superpositions with equal chance however totally different phases between the elements. The issue of 1/√2 is a normalization issue, which ensures that the entire chance of discovering the system in both state is 1.
We gained’t go deep into the arithmetic of Bell states, however their primary performance could be offered as:
- For |Φ⁺⟩ and |Φ⁻⟩ Bell states: For those who measure one qubit and discover it in state |0⟩, you immediately know the opposite qubit can also be in state |0⟩. For those who measure and discover the primary qubit in state |1⟩, the opposite qubit can even be in state |1⟩.
- For |Ψ⁺⟩ and |Ψ⁻⟩ Bell states: For those who measure one qubit and discover it in state |0⟩, you immediately know the opposite qubit is in state |1⟩. For those who measure and discover the primary qubit in state |1⟩, the opposite qubit will likely be in state |0⟩.
This distinctive property could be utilized for teleporting qubits’ states from one location to a different, which is vital in sharing personal keys via QKD and in superdense coding—a communication protocol that allows the transmission of two classical bits by sending only one qubit. Nonetheless, the property’s most typical present software is in quantum error correction. Right here, the correlation between entangled qubits aids in detecting and fixing errors with out the necessity for direct measurement of the quantum data, thereby sustaining the integrity of its quantum state.
Interference is the third property that provides quantum computing its edge. Quantum states could be represented as wave features as a result of wave-particle duality that defines quantum mechanics. Simply as quantum superposition permits qubits to exist in a state that embodies a continuum between 0 and 1, interference permits these superposed states to work together in methods that may be harnessed for computation.
Think about two musical notes being performed concurrently. Relying on their frequencies (pitches), they’ll produce numerous results. When the frequencies align in a harmonious method, the sound waves from every word mix to amplify the general sound, producing a pleasing and wealthy tone. If the frequencies barely mismatch, they’ll intrude destructively, making a dissonant sound. Simply as a posh piece of music entails a number of notes and harmonies interacting, a quantum system could be regarded as having a number of states or paths that intrude with each other.
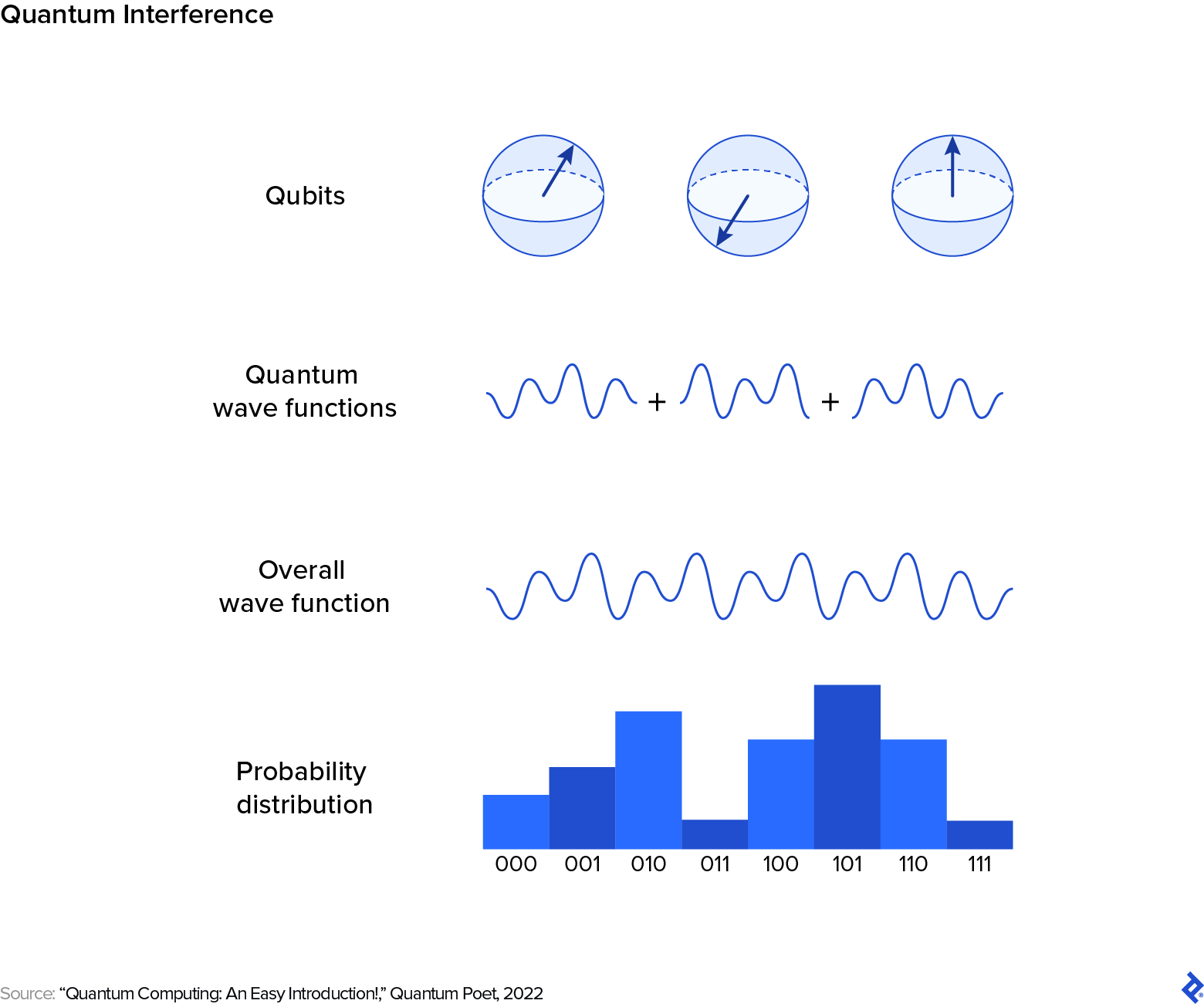
“We’ve developed strategies to make sure the wave amplitudes of the qubits that don’t correspond to the reply we’re searching for cancel out, whereas amplifying these equivalent to the specified end result. This course of leads to a state the place the chance of figuring out the right aspect is considerably excessive,” says Garrido-Gonzalez, whose work in quantum computing contains constructing a laser management system for quantum experiments on the College of Sussex. “The precision varies along with your system’s capabilities. In concept, rising the variety of qubits enhances the accuracy of the end result. Nonetheless, this introduces different challenges, like quantum decoherence, which impacts the soundness of knowledge in a quantum system when you measure it.”
In less complicated phrases, whereas quantum computer systems have the potential to unravel issues shortly, in addition they require cautious administration to keep up their accuracy as the extent of complexity—the variety of qubits in addition to the complexity of the question—will increase.
Layers of the Quantum Computing Stack
The layers of the quantum computing stack, very like the classical stack, comprise a number of ranges of abstraction, facilitating the transition from bodily {hardware} to high-level algorithmic options:
- {Hardware}: On the lowest stage, quantum computing {hardware} refers back to the bodily units that leverage quantum phenomena to carry out calculations. These can vary from small-scale quantum processors with a handful of qubits to extra superior programs with a whole lot or hundreds of qubits. {Hardware} might also contain applied sciences like superconducting qubits, trapped ions, topological qubits, or photonic circuits.
- Bodily qubits: These are the core elements of a quantum pc, representing the quantum model of classical bits. Nonetheless, bodily qubits are susceptible to errors and decoherence, resulting in potential knowledge corruption or loss.
- Quantum error correction: This layer focuses on figuring out and fixing errors in quantum knowledge attributable to decoherence and noise in bodily qubits. It normally requires spreading quantum data throughout a number of bodily qubits and making use of algorithms to right detected errors and get better the meant quantum state.
- Logical qubits: Logical qubits provide a extra steady and correct strategy to retailer quantum data, achieved via quantum error correction and different methods that decrease errors. An instruction set structure outlines the operations that may be executed on these logical qubits, offering a framework for quantum computing duties.
- Quantum intermediate illustration (QIR): QIR serves as a bridge between quantum algorithms and bodily {hardware}, permitting for the outline of quantum circuits and algorithms in a compiler-friendly method and for adaptability to numerous quantum computing applied sciences.
- Quantum algorithms: These are specialised directions or operations that leverage quantum concept—particularly phenomena like superposition, entanglement, and interference—to unravel issues effectively. Examples embody Shor’s algorithm for integer factorization and the group isomorphism algorithm.
Getting Fingers-on With Quantum Computing
To begin utilizing quantum software program, it is very important have a strong grasp of quantum data. However engineers getting into the quantum world don’t want an in-depth understanding of the physics behind quantum mechanics, says Ghassan Hallaq. “The basics are linear algebra, the vector area, and sophisticated numbers. Inside a posh vector area, quantum states are outlined as vectors, whereas matrices characterize quantum operations. Linear algebra provides the required instruments for understanding these representations and operations. Complicated numbers are additionally elementary, as they’re used to explain the chance amplitudes of quantum states,” Hallaq says.
To enhance the basics lined on this article, Hallaq recommends that newcomers to quantum growth discover a free collection of programs that IBM affords as further preparation for utilizing quantum software program. For now, we focus on the out there quantum software program growth kits (SDKs) for quantum computing, after which run via easy quantum growth examples utilizing Cirq and TensorFlow Quantum.
Obtainable Kits for Software program Growth
Builders aiming to program and interact with quantum computer systems have entry to numerous quantum software program growth kits and programming frameworks. These sources simplify the intricacies of quantum computing, permitting customers to make use of higher-level programming languages and libraries to craft and run quantum circuits and algorithms.
Two outstanding examples of simply out there quantum SDKs are Cirq and TensorFlow Quantum (TFQ), each developed by Google. Cirq is an open-source library that enables builders to create, manipulate, and optimize quantum circuits. Each researchers and builders engaged on the elemental features of quantum computing, akin to quantum algorithm design, quantum circuit optimization, and low-level quantum {hardware} management, will discover it exceptionally helpful.
TFQ is a Python framework that takes a unique method, specializing in integrating quantum computing into machine studying fashions and workflows. It’s constructed on high of TensorFlow, a staple in machine studying, and probably the most broadly used libraries within the discipline. TFQ gives a set of instruments and abstractions for developing quantum circuits, simulating quantum computations, and integrating these quantum computations with classical machine studying elements.
Whereas each Cirq and TFQ can interface with actual quantum computer systems via totally different again ends, Google doesn’t provide public entry to its quantum infrastructure right now. If you wish to check your circuits and algorithms in an actual machine, a preferred out there resolution is IBM’s Qiskit.
Qiskit goals to be approachable and straightforward to make use of, catering to customers who could not have a deep background in quantum computing. It permits builders to jot down quantum packages utilizing high-level programming languages like Python, providing a broad vary of options for circuit constructing, optimization, simulation, and visualization. IBM has constructed a sturdy ecosystem round Qiskit by partnering with companies in addition to analysis organizations and tutorial establishments. Different notable providers embody Microsoft’s Azure Quantum Growth Equipment and Amazon’s Braket, every providing distinctive options and capabilities.
Getting Began With Cirq
Cirq simplifies coping with the technicalities of quantum {hardware} platforms, enabling builders to create quantum algorithms and circuits on Google {hardware}. Google has supplied intensive sources to assist these excited about quantum computing rise up to hurry quickly.
Let’s take an preliminary take a look at code in a primary quantum algorithm. Our purpose is to outline and manipulate qubits via a sequence of quantum gates and operations. These manipulations occur inside a quantum circuit, a structured pathway that guides the evolution of qubits from their preliminary states to a ultimate measurement.
As talked about earlier, qubits can exist in a state of superposition, embodying each 0 and 1 concurrently. The primary job in developing our quantum circuit is to outline these qubits. In Cirq, qubits usually are not simply summary entities; they are often named, organized linearly, or positioned on a grid, mirroring potential layouts of bodily quantum processors. This flexibility permits us to tailor a circuit’s construction to the wants of particular algorithms or {hardware} configurations.
There are three major strategies for outlining qubits:
-
cirq.NamedQubit: Qubits are labeled by an summary identify. -
cirq.LineQubit: Qubits are labeled by a quantity in a linear array. -
cirq.GridQubit: Qubits are labeled by two numbers in an oblong grid.
That is an instance of find out how to outline qubits utilizing these three strategies:
# Naming qubits is a helpful follow, particularly in relation to summary algorithms and algorithms that aren't but mapped onto {hardware}.
q0 = cirq.NamedQubit('supply')
q1 = cirq.NamedQubit('goal')
# There are two methods to create line qubits:
# individually
q3 = cirq.LineQubit(3)
# or in a spread.
# This, for instance, will end in LineQubit(0), LineQubit(1), LineQubit(2).
q0, q1, q2 = cirq.LineQubit.vary(3)
# Grid qubits could be referenced individually.
q4_5 = cirq.GridQubit(4, 5)
# Alternatively, they are often created in bulk in a sq..
# This may create 16 qubits from (0,0) to (3,3).
qubits = cirq.GridQubit.sq.(4)
With our qubits outlined, we then introduce quantum gates, the dynamic forces that change the state of qubits. Quantum gates are to qubits what operations are to classical bits. In Cirq, a gate is outlined as an impact that may be utilized to a set of qubits, remodeling them into operations. These operations are the precise occasions that happen within the circuit, akin to flipping a qubit’s state or entangling two qubits collectively.
Within the subsequent instance, we’ll outline a circuit wherein two widespread gates will act on a pair of qubits:
-
Pauli-X gate: Sometimes called the bit-flip gate, it serves the identical goal because the classical NOT gate, flipping the state of a qubit;
|0⟩turns into|1⟩, and vice versa. -
Hadamard gate: The Hadamard gate creates superposition. It transforms the idea states
|0⟩and|1⟩into equal superpositions of each, enabling parallel computation over the superposed states.
After making use of the gates, we’ll measure the outcomes. Measuring is essential for collapsing the quantum state right into a classical state that exhibits us the influence of the quantum operations carried out on the qubits. With out measurement, whereas the qubits could bear numerous transformations, the end result of those operations can’t be decided.
import cirq
# Outline qubits.
q0, q1 = cirq.LineQubit.vary(2)
# Outline a gate.
X_gate = cirq.X # The Pauli-X gate
# Apply the gate to a qubit to create an operation.
x_op = X_gate(q0) # Apply the X gate to qubit q0
# Outline one other gate.
H_gate = cirq.H # The Hadamard gate
# Apply the gate to a qubit to create an operation.
h_op = H_gate(q0) # Apply the H gate to qubit q0
# Create a circuit and add operations.
circuit = cirq.Circuit()
circuit.append(x_op) # Add the X operation on q0
circuit.append(h_op) # Add the H operation on q0
circuit.append(cirq.measure(q0, q1)) # Measure each qubits
print("Circuit:")
print(circuit)
This printed output represents the sequence of operations within the circuit for every qubit:
Circuit:
0: ───X───H───M───
1: ───M───────
Right here:
- 0 and 1 point out the road (or qubit) numbers.
- X represents the Pauli-X gate utilized to qubit q0.
- H represents the Hadamard gate utilized to qubit q0 instantly after the Pauli-X gate.
- M signifies a measurement operation. The measurement is proven on each qubits, indicating that the state of each qubits q0 and q1 will likely be measured on the finish of the circuit execution.
Allow us to think about that each qubits begin within the state |0⟩. The Pauli-X gate flips q0 from |0⟩ to |1⟩. Then the Hadamard gate creates a superposition, remodeling the state of q0 |1⟩ right into a superposition of |0⟩ and |1⟩ with equal chances however with a section distinction. When measuring, q0 can collapse to both |0⟩ or |1⟩. Since q1 has not been altered and stays in state |0⟩, the measurement outcomes for the 2 qubits might theoretically be both:
- [0,0] with 50% chance.
- [1,0] with 50% chance.
The precise printout from executing the circuit wouldn’t present these chances however as a substitute one of many potential measurement outcomes, relying on the inherent randomness of quantum measurement in superposition states.
Whereas this circuit is extraordinarily primary, it demonstrates some elementary quantum computing ideas that function primary constructing blocks. As an illustration, one of many steps in Grover’s search algorithm entails making use of a Hadamard gate to every qubit within the system, placing every particular person qubit right into a superposition of states.
Executing a Cirq Circuit
Up to now we’ve not run the circuit, however outlined what it ought to do. To see precise outcomes, we should contain a quantum simulator or an actual quantum pc within the combine. Quantum simulators are software program instruments that emulate a quantum pc whereas nonetheless counting on classical computing sources. The simulator will execute the circuit a specified variety of instances and supply the measurement outcomes for every run, permitting you to investigate the chance distribution of the outcomes.
Cirq gives totally different simulators. For primary circuits, cirq.Simulator is an effective alternative:
import cirq
# If 'circuit' is our quantum circuit
simulator = cirq.Simulator()
outcome = simulator.run(circuit, repetitions=1000)
print(outcome)
After executing our circuit (the place one qubit had a Hadamard gate utilized) and working it for 1,000 repetitions, you would possibly see the next measurement output:
- [0,0]: 498 instances
- [1,0]: 502 instances
These outcomes are consistent with the anticipated theoretical chances.
Operating the circuit in an actual quantum pc is not going to be a lot totally different, however outcomes would possibly fluctuate from these predicted by preferrred simulators because of bodily noise and errors nonetheless widespread in quantum processors. It’ll even be dearer, and you might want to make certain that your circuit is suitable with any {hardware} constraints such because the out there qubit connections and supported gates.
Selecting between a simulator and an actual quantum pc typically relies on the stage of growth and the aims of your venture, in addition to the complexity of the circuit and the extent of precision you require. Preliminary growth, testing, and studying are effectively carried out on simulators, whereas ultimate validation, experiments demonstrating quantum benefit, and investigations into the consequences of noise and quantum {hardware} traits necessitate the usage of actual quantum processors.
Exploring TensorFlow Quantum
For instance the capabilities of TFQ, let’s construct upon the Cirq instance and introduce two new quantum gates: the controlled-NOT (CNOT) gate, which is essential for creating entanglement between qubits, and the RY gate, a single-qubit gate that rotates a qubit across the y-axis of the Bloch sphere. By adjusting the rotation angle θ (theta), you possibly can management the possibilities of measuring the qubit within the ∣0⟩ or ∣1⟩ state, enabling a wider and extra complicated vary of quantum operations.
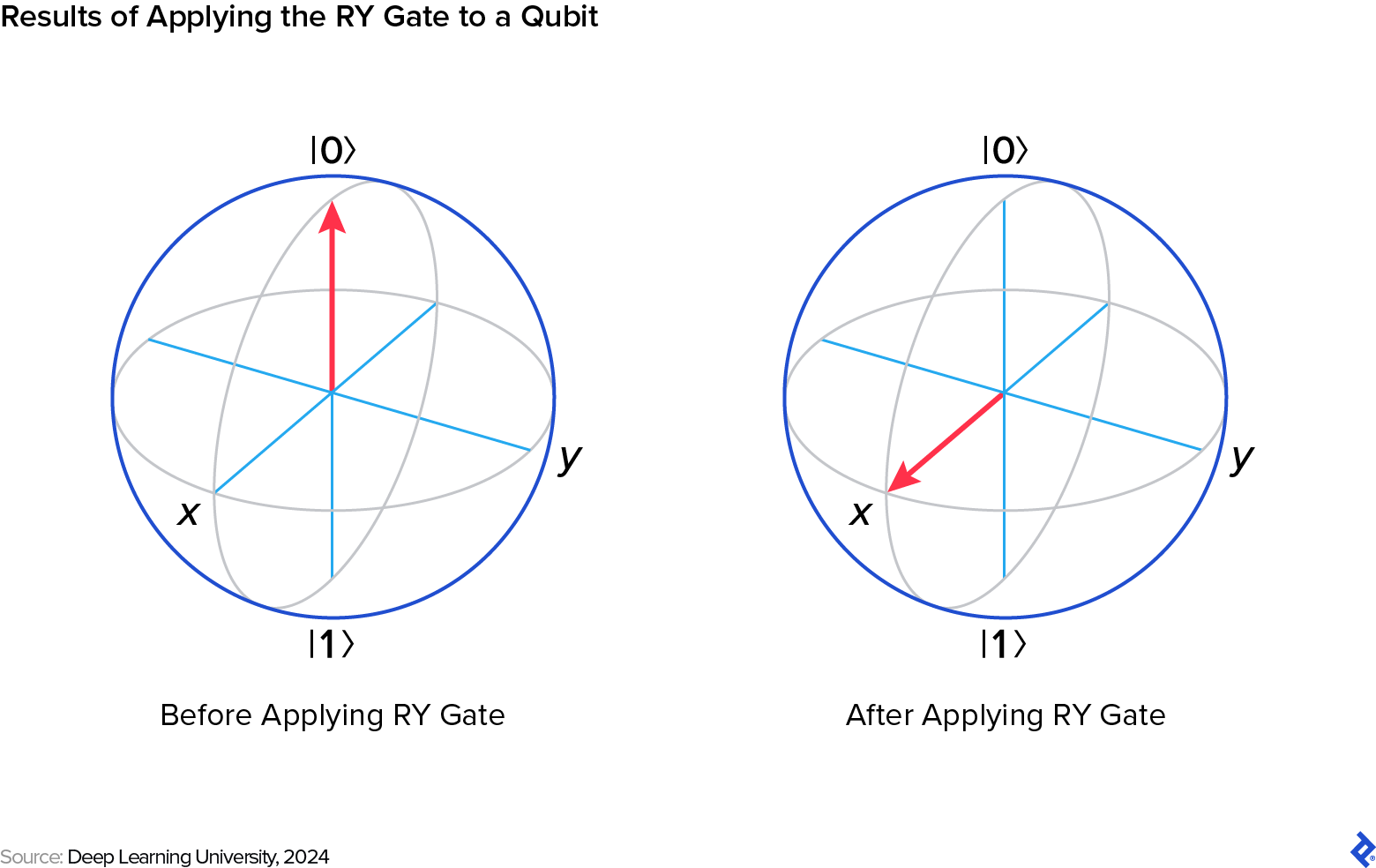
We initially outline a quantum circuit that applies a Hadamard gate to the primary qubit in an effort to create a superposition, then rotate it utilizing an RY gate, demonstrating how classical knowledge (on this case, the parameter for an RY gate) could be encoded right into a quantum state. Lastly, we use a CNOT gate to entangle it with the second qubit, making a Bell state and showcasing the three important properties of quantum computing.
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_quantum as tfq
import sympy
import cirq
# Outline qubits.
q0, q1 = cirq.LineQubit.vary(2)
# Outline symbols for parameterized gate.
theta = sympy.Image('theta')
# Create a circuit.
circuit = cirq.Circuit(
cirq.H(q0), # Apply Hadamard gate to create superposition
cirq.CNOT(q0, q1), # Entangle q0 and q1
cirq.ry(theta)(q0) # Apply RY gate with a parameter theta
)
# Visualize the circuit.
SVGCircuit(circuit)
That is what our circuit appears to be like like at this second:
Circuit:
0: ───H───RY(θ)───@───M───
│
1: ──────────────X───M───
Right here:
- 0 and 1 point out the road numbers equivalent to the primary and second qubits, respectively.
- H stands for the Hadamard gate that’s utilized to the primary qubit (q0). H places q0 right into a superposition state.
- RY(θ) signifies a rotation across the y-axis utilized to q0, parameterized by θ (theta). This represents find out how to encode classical knowledge into the quantum state utilizing the rotation angle.
- @ and X collectively signify the CNOT gate, with q0 appearing because the management qubit and q1 because the goal qubit. This gate entangles q0 and q1.
- M signifies measurement operations on each qubits. Measuring the qubits collapses their quantum state to classical bits.
Now let’s incorporate this quantum circuit right into a hybrid quantum-classical mannequin that may course of the classical knowledge (theta) via the quantum circuit after which classify it utilizing a classical neural community:
# Convert the circuit to a TensorFlow Quantum circuit.
q_data_encoding_circuit = tfq.convert_to_tensor([circuit])
# Outline a classical neural community.
mannequin = tf.keras.Sequential([
# Quantum layer: Encode data and apply quantum gates.
tfq.layers.ControlledPQC(circuit, operators=cirq.Z(q1), # Measure Z expectation values
control_values=tf.constant([[1.0]]), # Management values for theta
control_symbols=[theta]), # Symbols to manage
# Classical dense layer for classification
tf.keras.layers.Dense(2, activation='softmax')
])
# Compile the mannequin.
mannequin.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Assuming x_train and y_train are ready,
# the place x_train is the array of theta values for the information samples
# and y_train is the corresponding labels (0 or 1).
mannequin.match(x_train, y_train, epochs=10, batch_size=32)
The ControlledPQC layer in TFQ permits for the usage of parameterized quantum circuits wherein classical knowledge can management quantum operations, bridging the hole between classical and quantum computing. The advantages of this integration might not be evident at first sight, as this instance merely scratches the floor of what’s potential with TFQ and hybrid fashions, so let’s theorize a few sensible software.
In drug discovery, figuring out molecules with the potential to bind to particular protein targets is a posh and computationally intensive job. The method entails analyzing huge databases of chemical compounds to foretell their interactions with organic targets, which is essential for figuring out promising drug candidates. The high-dimensional nature of molecular knowledge and the complicated, nonlinear interactions between molecules and organic targets make this job very difficult for classical machine studying fashions.
However by utilizing an RY gate in a quantum circuit just like the one above to encode classical molecular knowledge (akin to molecular fingerprints) into quantum states, we are able to map the high-dimensional knowledge right into a state that displays the molecule’s traits.
Then, by making use of quantum operations to those encoded states, we are able to carry out computations that discover the complexity of the molecular knowledge. This step might contain utilizing quantum interference to spotlight patterns which might be indicative of a molecule’s binding affinity to the goal protein, for instance.
The quantum-processed knowledge is then fed right into a classical neural community, which classifies the molecules primarily based on their predicted binding affinity. The quantum preprocessing step goals to boost the function set, making it simpler for the classical neural community to establish promising drug candidates.
This method might considerably pace up the preliminary screening course of for drug candidates, permitting researchers to spend extra time investigating the compounds that look most promising.
Whereas we lined a easy instance, TFQ gives a wealthy set of instruments and abstractions for developing extra complicated hybrid quantum-classical fashions, enabling builders to discover the potential of quantum computing for enhancing machine studying algorithms and fashions.
Reaching Quantum Supremacy
Quantum computing is in attain for any developer who desires to begin studying and experimenting, however a number of challenges stay earlier than we are able to absolutely harness the potential of this know-how. Even with the highly effective algorithms and strategies out there, the {hardware} will not be but steady sufficient to achieve “quantum supremacy,” the theoretical second a quantum algorithm solves an issue that’s unfeasible or would require an unfeasible period of time to unravel for the perfect identified or potential classical algorithm for that job.
Some of the urgent points is quantum {hardware}’s present error charges and restricted coherence instances. Qubits are extraordinarily delicate to exterior disturbances and decoherence, resulting in errors and noise affecting quantum computations.
Researchers are diligently engaged on error correction methods and approaches to realize fault-tolerant quantum computing. Moreover, there’s a concerted push towards growing supplies and designs for quantum {hardware} to increase qubit coherence instances and decrease error charges.
Regardless of these challenges, quantum computing is an extremely promising prospect—and ongoing analysis and growth efforts are pushing the boundaries of computing as we all know it. Researchers are exploring the potential of quantum communication and quantum networking, which might allow safe and tamper-proof communication channels and distributed quantum computing capabilities. Integrating quantum computing with rising applied sciences like machine studying and synthetic intelligence might result in game-changing breakthroughs. Likewise, hybrid quantum-classical fashions and quantum-enhanced algorithms are anticipated to convey breakthroughs in fields like pc imaginative and prescient, pure language processing, and scientific simulations.
Because the quantum revolution unfolds, companies, researchers, and policymakers should keep knowledgeable and engaged with this quickly evolving discipline. By embracing quantum computing and fostering a tradition of innovation, organizations can place themselves to harness the transformative energy of this know-how and unlock new frontiers in product growth and technological development.