
A brand new malware distribution marketing campaign makes use of pretend Google Chrome, Phrase, and OneDrive errors to trick customers into working malicious PowerShell “fixes” that set up malware.
The brand new marketing campaign was noticed being utilized by a number of risk actors, together with these behind ClearFake, a brand new assault cluster known as ClickFix, and the TA571 risk actor, recognized for working as a spam distributor that sends giant volumes of e mail, resulting in malware and ransomware infections.
Earlier ClearFake assaults make the most of web site overlays that immediate guests to put in a pretend browser replace that installs malware.
Risk actors additionally make the most of JavaScript in HTML attachments and compromised web sites within the new assaults. Nevertheless, now the overlays show pretend Google Chrome, Microsoft Phrase, and OneDrive errors.
These errors immediate the customer to click on a button to repeat a PowerShell “repair” into the clipboard after which paste and run it in a Run: dialog or PowerShell immediate.
“Though the assault chain requires vital person interplay to achieve success, the social engineering is intelligent sufficient to current somebody with what seems to be like an actual downside and resolution concurrently, which can immediate a person to take motion with out contemplating the danger,” warns a new report from ProofPoint.
The payloads seen by Proofpoint embody DarkGate, Matanbuchus, NetSupport, Amadey Loader, XMRig, a clipboard hijacker, and Lumma Stealer.
PowerShell “repair” results in malware
Proofpoint analysts noticed three assault chains that differentiate primarily on their preliminary phases, with solely the primary not being attributed with excessive confidence to TA571.
On this first case, related to the risk actors behind ClearFake, customers go to a compromised web site that masses a malicious script hosted on the blockchain by way of Binance’s Sensible Chain contracts.
This script performs some checks and shows a pretend Google Chrome warning stating an issue displaying the webpage. The dialog then prompts the customer to put in a “root certificates” by copying a PowerShell script into the Home windows Clipboard and working it in a Home windows PowerShell (Admin) console.
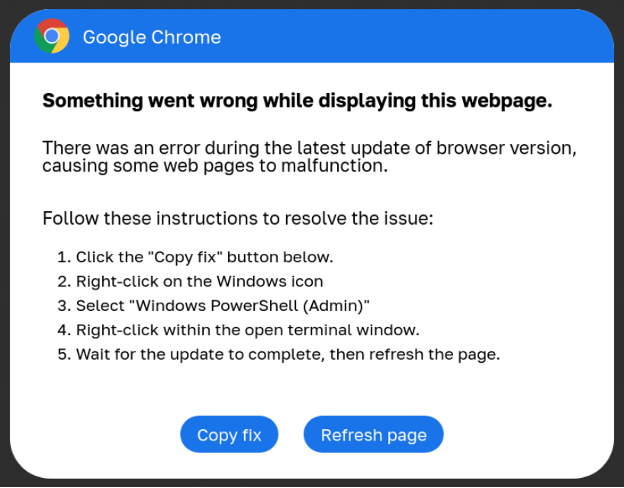
Supply: Proofpoint
When the PowerShell script is executed, it can carry out varied steps to substantiate the gadget is a legitimate goal, after which it can obtain extra payloads, as outlined beneath.
- Flushes the DNS cache.
- Removes clipboard content material.
- Shows a decoy message.
- Downloads one other distant PowerShell script, which performs anti-VM checks earlier than downloading an info-stealer.
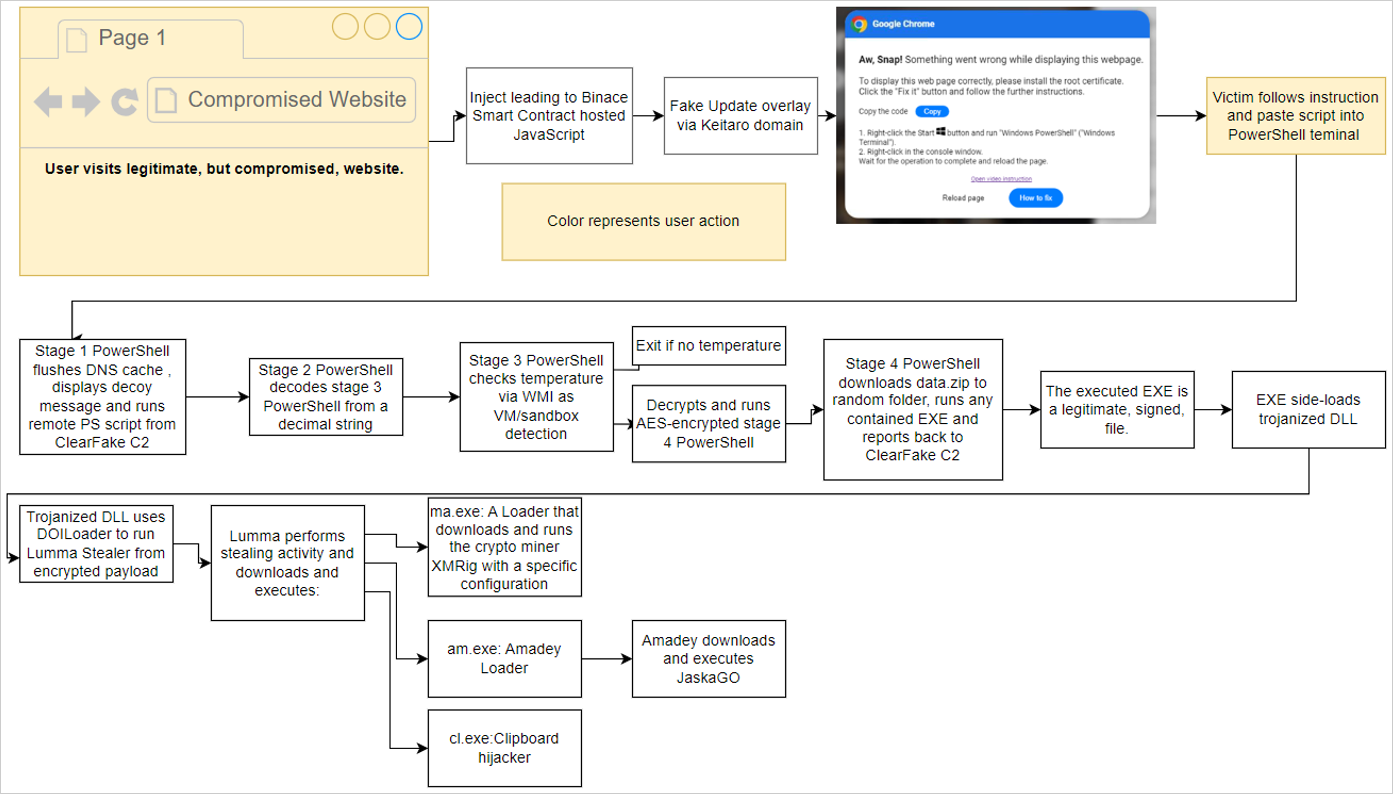
Supply: Proofpoint
The second assault chain is related to the ‘ClickFix’ marketing campaign and makes use of an injection on compromised web sites that creates an iframe to overlay one other pretend Google Chrome error.
Customers are instructed to open “Home windows PowerShell (Admin)” and paste the supplied code, resulting in the identical infections talked about above.
Lastly, an email-based an infection chain utilizing HTML attachments resembling Microsoft Phrase paperwork prompts customers to put in the “Phrase On-line” extension to view the doc accurately.
The error message provides ” repair” and “Auto-fix” choices, with ” repair” copying a base64-encoded PowerShell command to the clipboard, instructing the person to stick it into PowerShell.
Auto-fix” makes use of the search-ms protocol to show a WebDAV-hosted “repair.msi” or “repair.vbs” file on a distant attacker-controlled file share.
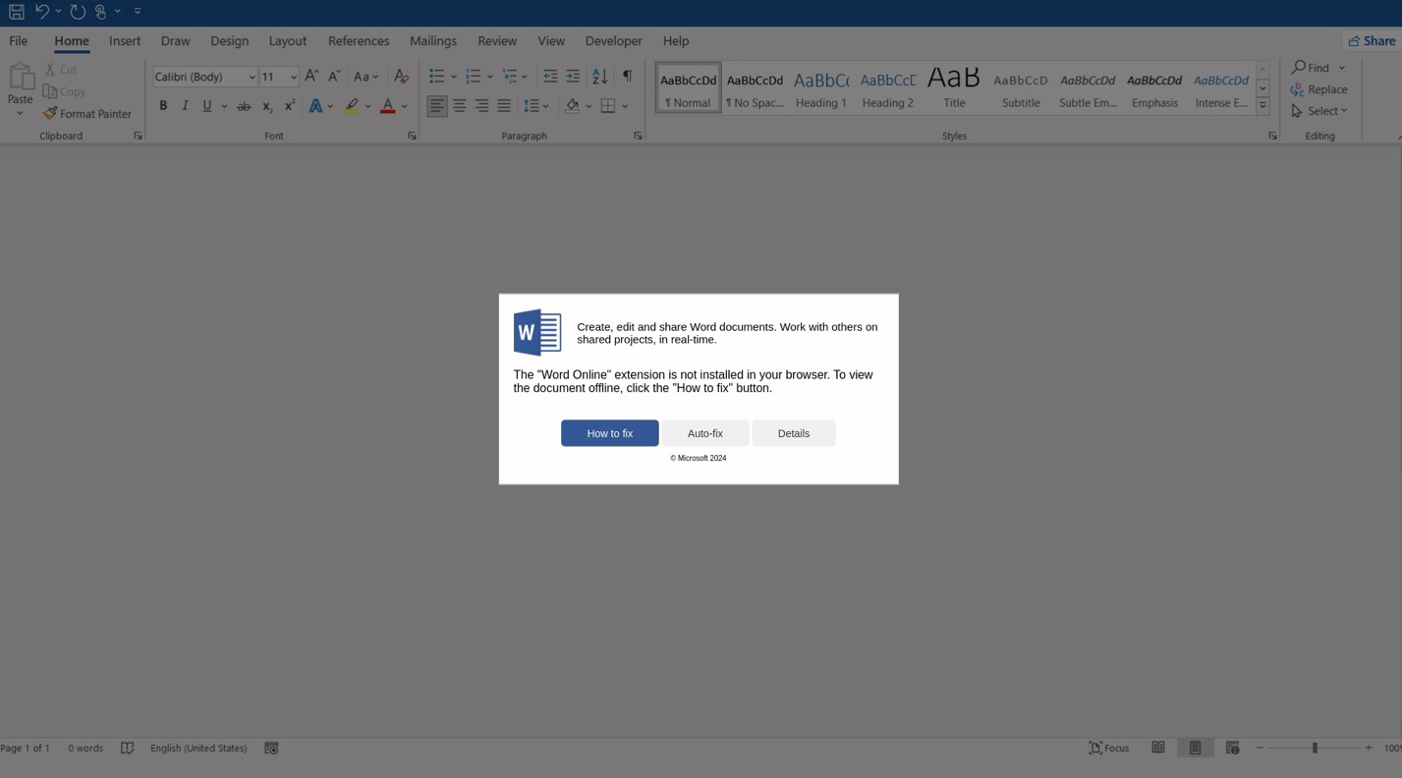
Supply: Proofpoint
On this case, the PowerShell instructions obtain and execute both an MSI file or a VBS script, resulting in Matanbuchus or DarkGate infections, respectively.
In all instances, the risk actors exploit their targets’ lack of understanding concerning the dangers of executing PowerShell instructions on their programs.
Additionally they make the most of Home windows’ incapability to detect and block the malicious actions initiated by the pasted code.
The completely different assault chains present that TA571 is actively experimenting with a number of strategies to enhance effectiveness and discover extra an infection pathways to compromise a bigger variety of programs.
