At Yoast, we speak loads about writing and readability. We take into account it a vital a part of search engine optimization. Your textual content must be simple to comply with and it must fulfill your customers’ wants. This focus in your consumer will assist your rankings. Nonetheless, we not often discuss how engines like google like Google learn and perceive these texts. On this publish, we’ll discover what we find out about how Google analyzes your on-line content material.
Are we positive Google understands textual content?
We all know that Google understands textual content to a point. Simply give it some thought. One of the essential issues Google has to do is match what somebody sorts into the search bar to an acceptable search outcome. Consumer indicators (like click-through and bounce charges) alone gained’t assist Google to do that correctly. Furthermore, we all know that it’s attainable to rank for a key phrase that you simply don’t use in your textual content (though it’s nonetheless good apply to determine and use a number of particular key phrases). So clearly, Google does one thing to truly learn and assess your textual content ultimately or one other.
How Google understands textual content
Again to our preliminary query: How does Google perceive textual content? To be sincere, we don’t know this intimately. Sadly, that info isn’t freely obtainable. And we additionally know, that Google is repeatedly evolving their capacity to grasp textual content on-line. However there are some clues that we are able to draw conclusions from. We all know that Google has taken large steps relating to understanding context. We additionally know that the search engine tries to find out how phrases and ideas are associated to one another. How do we all know this? By maintaining a tally of any information surrounding Google’s algorithm and contemplating how the precise search outcomes pages have modified.
Phrase embeddings
One fascinating method Google has filed patents for and labored on known as phrase embedding. The objective is to search out out what phrases are carefully associated to different phrases. A pc program is fed a specific amount of textual content. It then analyzes the phrases in that textual content and determines what phrases have a tendency to look collectively. Then, it interprets each phrase right into a collection of numbers. This permits the phrases to be represented as a degree in area in a diagram, like a scatter plot. This diagram reveals what phrases are associated in what methods. Extra precisely, it reveals the gap between phrases, form of like a galaxy made up of phrases. So for instance, a phrase like “key phrases” can be a lot nearer to “copywriting” than it might be to say “kitchen utensils”.
Apparently, this may also be accomplished for phrases, sentences and paragraphs. The larger the dataset you feed this system, the higher will probably be in a position to categorize and perceive phrases and work out how they’re used and what they imply. And, what have you learnt, Google has a database of your complete web. With a dataset like that, it’s attainable to create very dependable fashions that predict and assess the worth of textual content and context.
From phrase embeddings, it’s solely a small step to the idea of associated entities. Let’s check out the search outcomes as an instance what associated entities are. If you happen to kind in “varieties of pasta”, that is what you’ll see proper on the high of the SERP: a heading referred to as “pasta varieties”, with numerous wealthy outcomes that embrace a ton of various kinds of pasta. These pasta varieties are even subcategorized into “ribbon pasta”, “tubular pasta”, and different subtypes of pasta. And there are many comparable SERPs that replicate how phrases and ideas are associated to one another.
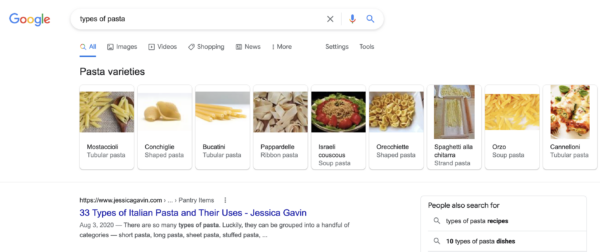
The associated entities patent that Google has filed truly mentions the associated entities index database. It is a database that shops ideas or entities, like pasta. These entities even have traits. Lasagna, for instance, is a pasta. It’s additionally made from dough. And it’s meals. Now, by analyzing the traits of entities, they are often grouped and categorized in every kind of various methods. This permits Google to grasp how phrases are associated, and, subsequently, to grasp context.
Google has closely invested in NLP
Pure language processing is the understanding of language by machines. It is among the hardest components of pc science and one the place essentially the most advances are being made. At the moment, with a world more and more powered by techniques run by AI, correct language understanding is essential. Google understands this and invests a ton within the growth of NLP fashions. One key system was BERT, a mannequin that might perceive the textual content coming after the content material phrases and earlier than these phrases. This fashion, the system has the total context of a sentence to make correct sense of its that means. What BERT did is superior, however Google is doing extra. Meet MUM.
MUM: Google’s language mannequin
In 2021, Google launched a brand new language mannequin that may multitask: MUM. Which means this mannequin can learn textual content, perceive its that means, type a deeper data concerning the topic, use different media to complement that data, get insights from greater than 75 languages and translate every little thing into content material that solutions complicated search queries. All on the identical time.
Does the rise of AI change all of this?
Over the previous 12 months, we’ve seen numerous developments within the space of AI. Naturally, Google couldn’t keep behind and launched their very own set of instruments together with the well-known AI mannequin Gemini. Most lately, they launched AI overviews of their search engine. And also you may need already guessed it, however pure language processing fashions turn out to be useful if you’re growing AI options. So Google’s ongoing analysis into NLP and machine studying is just not slowing down anytime quickly.
Sensible conclusions
So, how does Google perceive textual content precisely? What we all know leads us to 2 essential factors:
1. Context is essential
If Google understands context, it’s more likely to assess and choose context as nicely. The higher your copy matches Google’s notion of the context, the higher its possibilities of rating nicely. So skinny copy with a restricted scope goes to be at an obstacle. You’ll want to cowl your matters correctly and in sufficient element. And on a bigger scale, masking associated ideas and presenting a full physique of labor in your website will reinforce your authority on the subject you write about and specialise in.
2. Write to your reader
Texts which might be simple to learn and replicate relationships between ideas don’t simply profit your readers, they assist Google as nicely. Troublesome, inconsistent and poorly structured writing is extra obscure for each people and machines. You may assist the search engine perceive your texts by specializing in:
- Readability: making your textual content as simple to learn as attainable with out compromising your message.
- Correct construction: including clear subheadings and utilizing transition phrases.
- Good content material: including clear explanations that present how what you’re saying pertains to what’s already recognized a couple of subject.
The higher you do, the better your customers and Google will perceive your textual content and what it tries to realize. Which additionally helps you rank with the precise pages when a consumer sorts in a sure search question. Particularly as a result of Google is mainly making a mannequin that mimics the best way people course of language and data.
Google needs to be a reader
Ultimately, it boils right down to this: Google is turning into an increasing number of like an precise reader. By writing wealthy content material that’s well-structured and simple to learn and embedded into the context of the subject at hand, you’ll enhance your possibilities of doing nicely within the search outcomes.
Learn extra: search engine optimization copywriting: the last word information »

