Many growth groups flip to DynamoDB for constructing event-driven architectures and user-friendly, performant purposes at scale. As an operational database, DynamoDB is optimized for real-time transactions even when deployed throughout a number of geographic areas. Nevertheless, it doesn’t present robust efficiency for search and analytics entry patterns.
Search and Analytics on DynamoDB
Whereas NoSQL databases like DynamoDB typically have glorious scaling traits, they assist solely a restricted set of operations which might be centered on on-line transaction processing. This makes it troublesome to look, filter, mixture and be part of knowledge with out leaning closely on environment friendly indexing methods.
DynamoDB shops knowledge underneath the hood by partitioning it over numerous nodes based mostly on a user-specified partition key subject current in every merchandise. This user-specified partition key may be optionally mixed with a form key to signify a major key. The first key acts as an index, making question operations cheap. A question operation can do equality comparisons (=)
on the partition key and comparative operations (>, <, =, BETWEEN) on the type key if specified.
Performing analytical queries not coated by the above scheme requires the usage of a scan operation, which is usually executed by scanning over your entire DynamoDB desk in parallel. These scans may be gradual and costly by way of learn throughput as a result of they require a full learn of your entire desk. Scans additionally are inclined to decelerate when the desk measurement grows, as there’s
extra knowledge to scan to supply outcomes. If we wish to assist analytical queries with out encountering prohibitive scan prices, we will leverage secondary indexes, which we’ll focus on subsequent.
Indexing in DynamoDB
In DynamoDB, secondary indexes are sometimes used to enhance software efficiency by indexing fields which might be queried regularly. Question operations on secondary indexes can be used to energy particular options by analytic queries which have clearly outlined necessities.
Secondary indexes consist of making partition keys and non-compulsory kind keys over fields that we wish to question. There are two varieties of secondary indexes:
- Native secondary indexes (LSIs): LSIs prolong the hash and vary key attributes for a single partition.
- World secondary indexes (GSIs): GSIs are indexes which might be utilized to a complete desk as an alternative of a single partition.
Nevertheless, as Nike found, overusing GSIs in DynamoDB may be costly. Analytics in DynamoDB, except they’re used just for quite simple level lookups or small vary scans, may end up in overuse of secondary indexes and excessive prices.
The prices for provisioned capability when utilizing indexes can add up rapidly as a result of all updates to the bottom desk must be made within the corresponding GSIs as effectively. The truth is, AWS advises that the provisioned write capability for a worldwide secondary index needs to be equal to or higher than the write capability of the bottom desk to keep away from throttling writes to the bottom desk and crippling the applying. The price of provisioned write capability grows linearly with the variety of GSIs configured, making it price prohibitive to make use of many GSIs to assist many entry patterns.
DynamoDB can also be not well-designed to index knowledge in nested constructions, together with arrays and objects. Earlier than indexing the info, customers might want to denormalize the info, flattening the nested objects and arrays. This might enormously enhance the variety of writes and related prices.
For a extra detailed examination of utilizing DynamoDB secondary indexes for analytics, see our weblog Secondary Indexes For Analytics On DynamoDB.
The underside line is that for analytical use circumstances, you may achieve vital efficiency and price benefits by syncing the DynamoDB desk with a distinct software or service that acts as an exterior secondary index for operating advanced analytics effectively.
DynamoDB + Elasticsearch
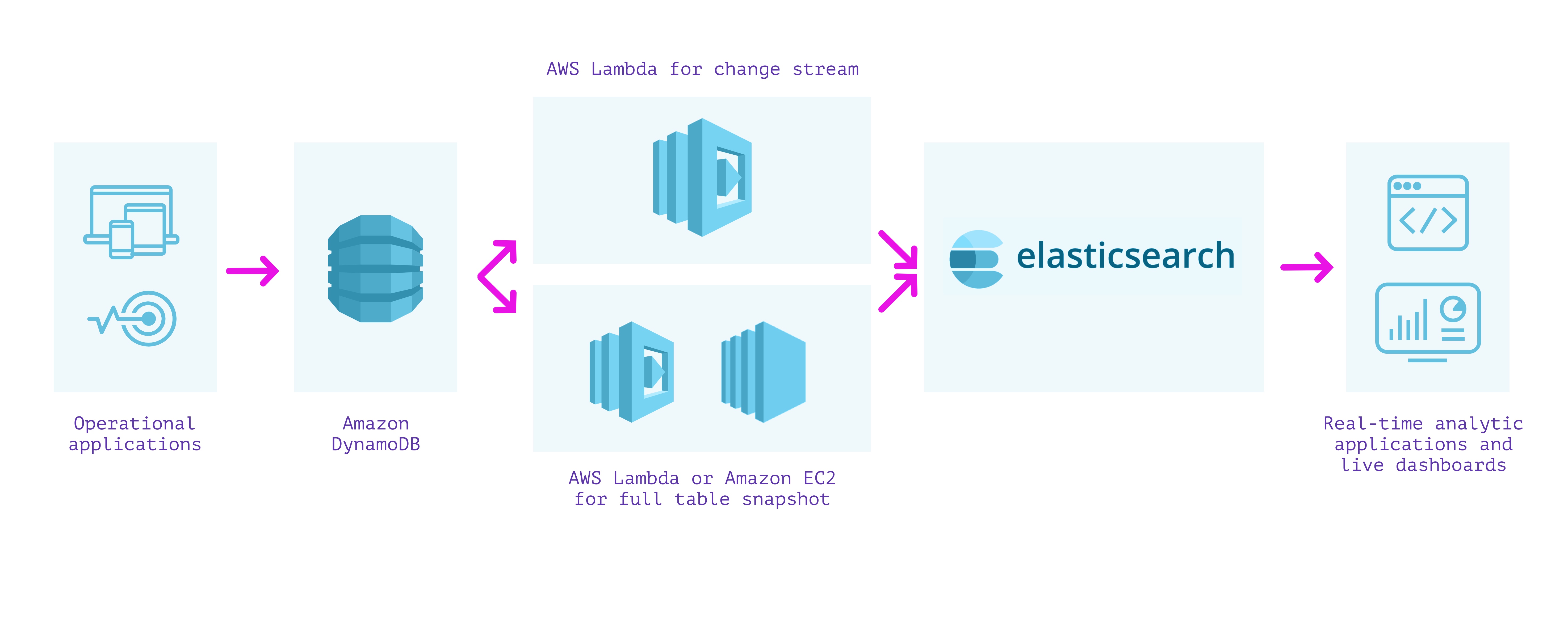
One strategy to constructing a secondary index over our knowledge is to make use of DynamoDB with Elasticsearch. Cloud-based Elasticsearch, corresponding to Elastic Cloud or Amazon OpenSearch Service, can be utilized to provision and configure nodes in response to the scale of the indexes, replication, and different necessities. A managed cluster requires some operations to improve, safe, and preserve performant, however much less so than operating it completely by your self on EC2 situations.
Because the strategy utilizing the Logstash Plugin for Amazon DynamoDB is unsupported and reasonably troublesome to arrange, we will as an alternative stream writes from DynamoDB into Elasticsearch utilizing DynamoDB Streams and an AWS Lambda operate. This strategy requires us to carry out two separate steps:
- We first create a lambda operate that’s invoked on the DynamoDB stream to submit every replace because it happens in DynamoDB into Elasticsearch.
- We then create a lambda operate (or EC2 occasion operating a script if it can take longer than the lambda execution timeout) to submit all the present contents of DynamoDB into Elasticsearch.
We should write and wire up each of those lambda features with the right permissions with a view to be sure that we don’t miss any writes into our tables. When they’re arrange together with required monitoring, we will obtain paperwork in Elasticsearch from DynamoDB and might use Elasticsearch to run analytical queries on the info.
The benefit of this strategy is that Elasticsearch helps full-text indexing and several other varieties of analytical queries. Elasticsearch helps purchasers in varied languages and instruments like Kibana for visualization that may assist rapidly construct dashboards. When a cluster is configured appropriately, question latencies may be tuned for quick analytical queries over knowledge flowing into Elasticsearch.
Disadvantages embody that the setup and upkeep price of the answer may be excessive. Even managed Elasticsearch requires coping with replication, resharding, index development, and efficiency tuning of the underlying situations.
Elasticsearch has a tightly coupled structure that doesn’t separate compute and storage. This implies assets are sometimes overprovisioned as a result of they can’t be independently scaled. As well as, a number of workloads, corresponding to reads and writes, will contend for a similar compute assets.
Elasticsearch additionally can’t deal with updates effectively. Updating any subject will set off a reindexing of your entire doc. Elasticsearch paperwork are immutable, so any replace requires a brand new doc to be listed and the previous model marked deleted. This leads to further compute and I/O expended to reindex even the unchanged fields and to put in writing whole paperwork upon replace.
As a result of lambdas hearth after they see an replace within the DynamoDB stream, they will have have latency spikes resulting from chilly begins. The setup requires metrics and monitoring to make sure that it’s appropriately processing occasions from the DynamoDB stream and capable of write into Elasticsearch.
Functionally, by way of analytical queries, Elasticsearch lacks assist for joins, that are helpful for advanced analytical queries that contain a couple of index. Elasticsearch customers typically must denormalize knowledge, carry out application-side joins, or use nested objects or parent-child relationships to get round this limitation.
Benefits
- Full-text search assist
- Help for a number of varieties of analytical queries
- Can work over the newest knowledge in DynamoDB
Disadvantages
- Requires administration and monitoring of infrastructure for ingesting, indexing, replication, and sharding
- Tightly coupled structure leads to useful resource overprovisioning and compute competition
- Inefficient updates
- Requires separate system to make sure knowledge integrity and consistency between DynamoDB and Elasticsearch
- No assist for joins between completely different indexes
This strategy can work effectively when implementing full-text search over the info in DynamoDB and dashboards utilizing Kibana. Nevertheless, the operations required to tune and keep an Elasticsearch cluster in manufacturing, its inefficient use of assets and lack of be part of capabilities may be difficult.
DynamoDB + Rockset
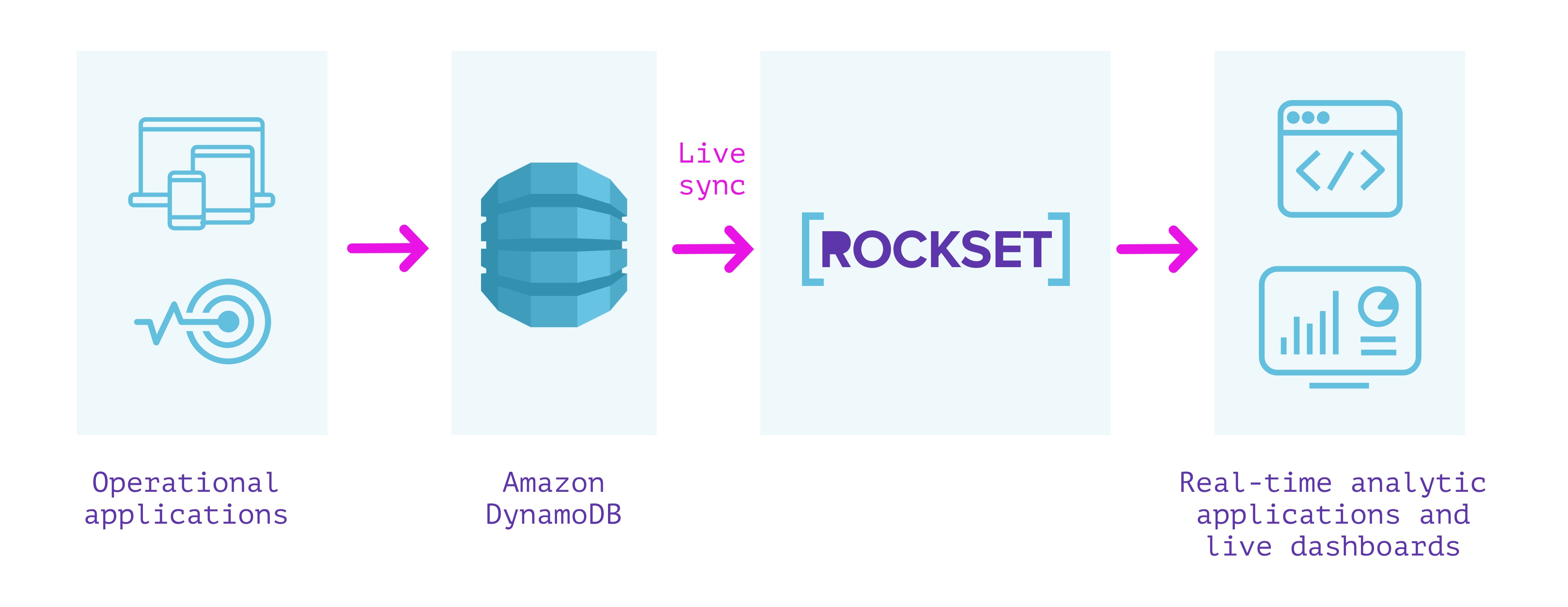
Rockset is a totally managed search and analytics database constructed primarily to assist real-time purposes with excessive QPS necessities. It’s typically used as an exterior secondary index for knowledge from OLTP databases.
Rockset has a built-in connector with DynamoDB that can be utilized to maintain knowledge in sync between DynamoDB and Rockset. We are able to specify the DynamoDB desk we wish to sync contents from and a Rockset assortment that indexes the desk. Rockset indexes the contents of the DynamoDB desk in a full snapshot after which syncs new modifications as they happen. The contents of the Rockset assortment are at all times in sync with the DynamoDB supply; no quite a lot of seconds aside in regular state.
Rockset manages the info integrity and consistency between the DynamoDB desk and the Rockset assortment routinely by monitoring the state of the stream and offering visibility into the streaming modifications from DynamoDB.
And not using a schema definition, a Rockset assortment can routinely adapt when fields are added/eliminated, or when the construction/sort of the info itself modifications in DynamoDB. That is made attainable by robust dynamic typing and good schemas that obviate the necessity for any further ETL.
The Rockset assortment we sourced from DynamoDB helps SQL for querying and may be simply utilized by builders with out having to study a domain-specific language. It can be used to serve queries to purposes over a REST API or utilizing shopper libraries in a number of programming languages. The superset of ANSI SQL that Rockset helps can work natively on deeply nested JSON arrays and objects, and leverage indexes which might be routinely constructed over all fields, to get millisecond latencies on even advanced analytical queries.
Rockset has pioneered compute-compute separation, which permits isolation of workloads in separate compute items whereas sharing the identical underlying real-time knowledge. This affords customers higher useful resource effectivity when supporting simultaneous ingestion and queries or a number of purposes on the identical knowledge set.
As well as, Rockset takes care of safety, encryption of information, and role-based entry management for managing entry to it. Rockset customers can keep away from the necessity for ETL by leveraging ingest transformations we will arrange in Rockset to switch the info because it arrives into a set. Customers may also optionally handle the lifecycle of the info by establishing retention insurance policies to routinely purge older knowledge. Each knowledge ingestion and question serving are routinely managed, which lets us give attention to constructing and deploying dwell dashboards and purposes whereas eradicating the necessity for infrastructure administration and operations.
Particularly related in relation to syncing with DynamoDB, Rockset helps in-place field-level updates, in order to keep away from expensive reindexing. Examine Rockset and Elasticsearch by way of ingestion, querying and effectivity to decide on the fitting software for the job.
Abstract
- Constructed to ship excessive QPS and serve real-time purposes
- Fully serverless. No operations or provisioning of infrastructure or database required
- Compute-compute separation for predictable efficiency and environment friendly useful resource utilization
- Stay sync between DynamoDB and the Rockset assortment, in order that they’re by no means quite a lot of seconds aside
- Monitoring to make sure consistency between DynamoDB and Rockset
- Automated indexes constructed over the info enabling low-latency queries
- In-place updates that avoids costly reindexing and lowers knowledge latency
- Joins with knowledge from different sources corresponding to Amazon Kinesis, Apache Kafka, Amazon S3, and so forth.
We are able to use Rockset for implementing real-time analytics over the info in DynamoDB with none operational, scaling, or upkeep issues. This may considerably velocity up the event of real-time purposes. If you would like to construct your software on DynamoDB knowledge utilizing Rockset, you will get began without cost on right here.
