Elasticsearch is an open-source, distributed JSON-based search and analytics engine constructed utilizing Apache Lucene with the aim of offering quick real-time search performance. It’s a NoSQL information retailer that’s document-oriented, scalable, and schemaless by default. Elasticsearch is designed to work at scale with massive information units. As a search engine, it supplies quick indexing and search capabilities that may be horizontally scaled throughout a number of nodes.
Shameless plug: Rockset is a real-time indexing database within the cloud. It mechanically builds indexes which might be optimized not only for search but in addition aggregations and joins, making it quick and simple to your purposes to question information, no matter the place it comes from and what format it’s in. However this publish is about highlighting some workarounds, in case you actually need to do SQL-style joins in Elasticsearch.
Why Do Knowledge Relationships Matter?
We reside in a extremely related world the place dealing with information relationships is vital. Relational databases are good at dealing with relationships, however with consistently altering enterprise necessities, the mounted schema of those databases leads to scalability and efficiency points. The usage of NoSQL information shops is turning into more and more well-liked as a consequence of their potential to sort out quite a few challenges related to the normal information dealing with approaches.
Enterprises are regularly coping with complicated information constructions the place aggregations, joins, and filtering capabilities are required to research the information. With the explosion of unstructured information, there are a rising variety of use circumstances requiring the becoming a member of of knowledge from completely different sources for information analytics functions.
Whereas joins are primarily an SQL idea, they’re equally vital within the NoSQL world as nicely. SQL-style joins aren’t supported in Elasticsearch as first-class residents. This text will focus on learn how to outline relationships in Elasticsearch utilizing numerous strategies corresponding to denormalizing, application-side joins, nested paperwork, and parent-child relationships. It can additionally discover the use circumstances and challenges related to every method.
Learn how to Cope with Relationships in Elasticsearch
As a result of Elasticsearch shouldn’t be a relational database, joins don’t exist as a local performance like in an SQL database. It focuses extra on search effectivity versus storage effectivity. The saved information is virtually flattened out or denormalized to drive quick search use circumstances.
There are a number of methods to outline relationships in Elasticsearch. Based mostly in your use case, you possibly can choose one of many under strategies in Elasticsearch to mannequin your information:
- One-to-one relationships: Object mapping
- One-to-many relationships: Nested paperwork and the parent-child mannequin
- Many-to-many relationships: Denormalizing and application-side joins
One-to-one object mappings are easy and won’t be mentioned a lot right here. The rest of this weblog will cowl the opposite two eventualities in additional element.
Need to study extra about Joins in Elasticsearch? Try our publish on widespread use circumstances
Managing Your Knowledge Mannequin in Elasticsearch
There are 4 widespread approaches to managing information in Elasticsearch:
- Denormalization
- Software-side joins
- Nested objects
- Guardian-child relationships
Denormalization
Denormalization supplies one of the best question search efficiency in Elasticsearch, since becoming a member of information units at question time isn’t essential. Every doc is unbiased and comprises all of the required information, thus eliminating the necessity for costly be a part of operations.
With denormalization, the information is saved in a flattened construction on the time of indexing. Although this will increase the doc dimension and leads to the storage of duplicate information in every doc. Disk area shouldn’t be an costly commodity and thus little trigger for concern.
Use Instances for Denormalization
Whereas working with distributed techniques, having to affix information units throughout the community can introduce vital latencies. You’ll be able to keep away from these costly be a part of operations by denormalizing information. Many-to-many relationships will be dealt with by information flattening.
Challenges with Knowledge Denormalization
- Duplication of knowledge into flattened paperwork requires further cupboard space.
- Managing information in a flattened construction incurs further overhead for information units which might be relational in nature.
- From a programming perspective, denormalization requires further engineering overhead. You’ll need to jot down further code to flatten the information saved in a number of relational tables and map it to a single object in Elasticsearch.
- Denormalizing information shouldn’t be a good suggestion in case your information modifications steadily. In such circumstances denormalization would require updating the entire paperwork when any subset of the information have been to vary and so ought to be averted.
- The indexing operation takes longer with flattened information units since extra information is being listed. In case your information modifications steadily, this could point out that your indexing price is increased, which might trigger cluster efficiency points.
Software-Aspect Joins
Software-side joins can be utilized when there’s a want to take care of the connection between paperwork. The info is saved in separate indices, and be a part of operations will be carried out from the applying facet throughout question time. This does, nonetheless, entail operating further queries at search time out of your software to affix paperwork.
Use Instances for Software-Aspect Joins
Software-side joins make sure that information stays normalized. Modifications are carried out in a single place, and there’s no must consistently replace your paperwork. Knowledge redundancy is minimized with this method. This methodology works nicely when there are fewer paperwork and information modifications are much less frequent.
Challenges with Software-Aspect Joins
- The appliance must execute a number of queries to affix paperwork at search time. If the information set has many customers, you will have to execute the identical set of queries a number of occasions, which might result in efficiency points. This method, subsequently, doesn’t leverage the true energy of Elasticsearch.
- This method leads to complexity on the implementation degree. It requires writing further code on the software degree to implement be a part of operations to ascertain a relationship amongst paperwork.
Nested Objects
The nested method can be utilized if it’s essential to preserve the connection of every object within the array. Nested paperwork are internally saved as separate Lucene paperwork and will be joined at question time. They’re index-time joins, the place a number of Lucene paperwork are saved in a single block. From the applying perspective, the block appears to be like like a single Elasticsearch doc. Querying is subsequently comparatively sooner, since all the information resides in the identical object. Nested paperwork take care of one-to-many relationships.
Use Instances for Nested Paperwork
Creating nested paperwork is most well-liked when your paperwork include arrays of objects. Determine 1 under exhibits how the nested kind in Elasticsearch permits arrays of objects to be internally listed as separate Lucene paperwork. Lucene has no idea of internal objects, therefore it’s attention-grabbing to see how Elasticsearch internally transforms the unique doc into flattened multi-valued fields.
One benefit of utilizing nested queries is that it gained’t do cross-object matches, therefore surprising match outcomes are averted. It’s conscious of object boundaries, making the searches extra correct.
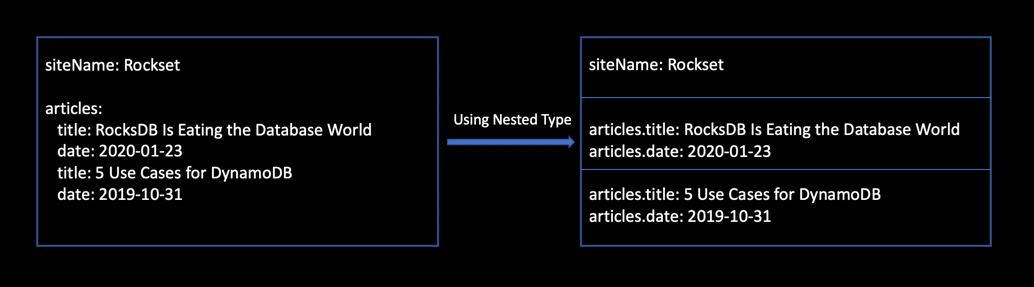
Determine 1: Arrays of objects listed internally as separate Lucene paperwork in Elasticsearch utilizing nested method
Challenges with Nested Objects
- The basis object and its nested objects have to be fully reindexed with a purpose to add/replace/delete a nested object. In different phrases, a toddler report replace will lead to reindexing the whole doc.
- Nested paperwork can’t be accessed instantly. They’ll solely be accessed by its associated root doc.
- Search requests return the whole doc as a substitute of returning solely the nested paperwork that match the search question.
- In case your information set modifications steadily, utilizing nested paperwork will lead to a lot of updates.
Guardian-Little one Relationships
Guardian-child relationships leverage the be a part of datatype with a purpose to fully separate objects with relationships into particular person paperwork—mother or father and baby. This allows you to retailer paperwork in a relational construction in separate Elasticsearch paperwork that may be up to date individually.
Guardian-child relationships are helpful when the paperwork should be up to date typically. This method is subsequently supreme for eventualities when the information modifications steadily. Principally, you separate out the bottom doc into a number of paperwork containing mother or father and baby. This permits each the mother or father and baby paperwork to be listed/up to date/deleted independently of each other.
Looking out in Guardian and Little one Paperwork
To optimize Elasticsearch efficiency throughout indexing and looking, the overall advice is to make sure that the doc dimension shouldn’t be massive. You’ll be able to leverage the parent-child mannequin to interrupt down your doc into separate paperwork.
Nevertheless, there are some challenges with implementing this. Guardian and baby paperwork should be routed to the identical shard in order that becoming a member of them throughout question time might be in-memory and environment friendly. The mother or father ID must be used because the routing worth for the kid doc. The _parent area supplies Elasticsearch with the ID and kind of the mother or father doc, which internally lets it route the kid paperwork to the identical shard because the mother or father doc.
Elasticsearch means that you can search from complicated JSON objects. This, nonetheless, requires an intensive understanding of the information construction to effectively question from it. The parent-child mannequin leverages a number of filters to simplify the search performance:
Returns mother or father paperwork which have baby paperwork matching the question.
Accepts a mother or father and returns baby paperwork that related mother and father have matched.
Fetches related kids info from the has_child question.
Determine 2 exhibits how you need to use the parent-child mannequin to reveal one-to-many relationships. The kid paperwork will be added/eliminated/up to date with out impacting the mother or father. The identical holds true for the mother or father doc, which will be up to date with out reindexing the kids.
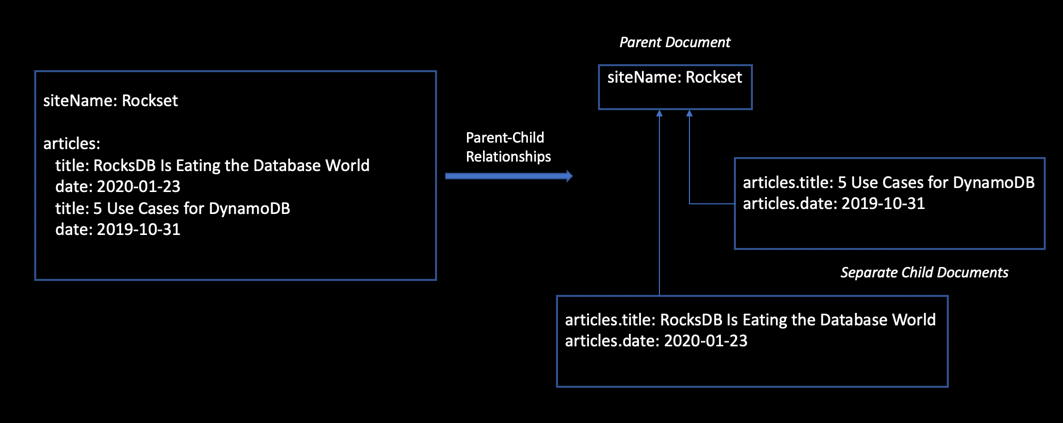
Determine 2: Guardian-child mannequin for one-to-many relationships
Challenges with Guardian-Little one Relationships
- Queries are dearer and memory-intensive due to the be a part of operation.
- There’s an overhead to parent-child constructs, since they’re separate paperwork that have to be joined at question time.
- Want to make sure that the mother or father and all its kids exist on the identical shard.
- Storing paperwork with parent-child relationships entails implementation complexity.
Conclusion
Choosing the proper Elasticsearch information modeling design is vital for software efficiency and maintainability. When designing your information mannequin in Elasticsearch, it is very important notice the varied execs and cons of every of the 4 modeling strategies mentioned herein.
On this article, we explored how nested objects and parent-child relationships allow SQL-like be a part of operations in Elasticsearch. You can even implement customized logic in your software to deal with relationships with application-side joins. To be used circumstances by which it’s essential to be a part of a number of information units in Elasticsearch, you possibly can ingest and cargo each these information units into the Elasticsearch index to allow performant querying.
Out of the field, Elasticsearch doesn’t have joins as in an SQL database. Whereas there are potential workarounds for establishing relationships in your paperwork, it is very important pay attention to the challenges every of those approaches presents.
Utilizing Native SQL Joins with Rockset
When there’s a want to mix a number of information units for real-time analytics, a database that gives native SQL joins can deal with this use case higher. Like Elasticsearch, Rockset is used as an indexing layer on information from databases, occasion streams, and information lakes, allowing schemaless ingest from these sources. Not like Elasticsearch, Rockset supplies the flexibility to question with full-featured SQL, together with joins, supplying you with better flexibility in how you need to use your information.

